Neurological manifestations of polyarteritis nodosa: a tour of the neuroaxis by case series
- PMID: 34020612
- PMCID: PMC8138997
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-021-02228-2
Neurological manifestations of polyarteritis nodosa: a tour of the neuroaxis by case series
Abstract
Background: Heterogenous central nervous system (CNS) neurologic manifestations of polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) are underrecognized. We review three cases of patients with PAN that illustrate a range of nervous system pathology, including the classical mononeuritis multiplex as well as uncommon brain and spinal cord vascular manifestations.
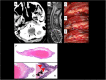
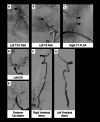
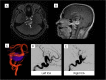
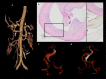
Case presentation: Case 1 presented with mononeuritis multiplex and characteristic skin findings. Case 2 presented with thunderclap headache and myelopathy due to spinal artery aneurysm rupture. Both patients experienced disease remission upon treatment. Case 3 presented with headache and bulbar symptoms due to partially thrombosed intracranial aneurysms, followed by systemic manifestations related to visceral aneurysms. She demonstrated clinical improvement with treatment, was lost to follow-up, then clinically deteriorated and entered hospice care.
Conclusions: Although the peripheral manifestations of PAN are well-known, PAN association with CNS neurovascular disease is relatively underappreciated. Clinician awareness of the spectrum of neurologic disease is required to reduce diagnostic delay and promote prompt diagnosis and treatment with immunosuppressants.
Keywords: Case series; Intracranial aneurysm; Multidisciplinary; Polyarteritis nodosa; Spinal artery aneurysm.
Conflict of interest statement
CFD reports funding from Microvention-Terumo, Inc., outside the submitted work.
CA reports grants from NIH NIAMS 5 T32 AR007304–40 during the conduct of the study.
There are no additional financial or non-financial competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Pagnoux C, Seror R, Henegar C, Mahr A, Cohen P, Le Guern V, et al. Clinical features and outcomes in 348 patients with polyarteritis nodosa: a systematic retrospective study of patients diagnosed between 1963 and 2005 and entered into the French Vasculitis study group database. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(2):616–626. doi: 10.1002/art.27240. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

