Clinical applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning in cancer diagnosis: looking into the future
- PMID: 34020642
- PMCID: PMC8139146
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-01981-1
Clinical applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning in cancer diagnosis: looking into the future
Abstract
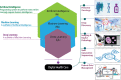
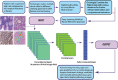
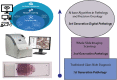
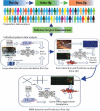
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the use of mathematical algorithms to mimic human cognitive abilities and to address difficult healthcare challenges including complex biological abnormalities like cancer. The exponential growth of AI in the last decade is evidenced to be the potential platform for optimal decision-making by super-intelligence, where the human mind is limited to process huge data in a narrow time range. Cancer is a complex and multifaced disorder with thousands of genetic and epigenetic variations. AI-based algorithms hold great promise to pave the way to identify these genetic mutations and aberrant protein interactions at a very early stage. Modern biomedical research is also focused to bring AI technology to the clinics safely and ethically. AI-based assistance to pathologists and physicians could be the great leap forward towards prediction for disease risk, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatments. Clinical applications of AI and Machine Learning (ML) in cancer diagnosis and treatment are the future of medical guidance towards faster mapping of a new treatment for every individual. By using AI base system approach, researchers can collaborate in real-time and share knowledge digitally to potentially heal millions. In this review, we focused to present game-changing technology of the future in clinics, by connecting biology with Artificial Intelligence and explain how AI-based assistance help oncologist for precise treatment.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Cancer diagnosis; Machine learning; Therapeutic interventions; Treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Deng L, Yu D. Deep learning: methods and applications. Found Trends Signal Process. 2014;7(34):197–387. doi: 10.1561/2000000039. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

