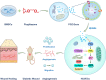
Exosomes derived from pioglitazone-pretreated MSCs accelerate diabetic wound healing through enhancing angiogenesis
- PMID: 34020670
- PMCID: PMC8139165
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-021-00894-5
Exosomes derived from pioglitazone-pretreated MSCs accelerate diabetic wound healing through enhancing angiogenesis
Abstract
Background: Enhanced angiogenesis can promote diabetic wound healing. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)-derived exosomes, which are cell-free therapeutics, are promising candidates for the treatment of diabetic wound healing. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of exosomes derived from MSCs pretreated with pioglitazone (PGZ-Exos) on diabetic wound healing.
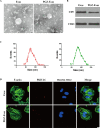
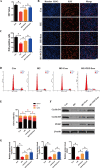
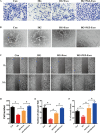
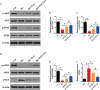
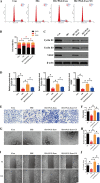
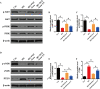
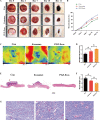
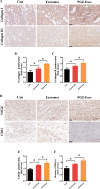
Results: We isolated PGZ-Exos from the supernatants of pioglitazone-treated BMSCs and found that PGZ-Exos significantly promote the cell viability and proliferation of Human Umbilical Vein Vascular Endothelial Cells (HUVECs) injured by high glucose (HG). PGZ-Exos enhanced the biological functions of HUVECs, including migration, tube formation, wound repair and VEGF expression in vitro. In addition, PGZ-Exos promoted the protein expression of p-AKT, p-PI3K and p-eNOS and suppressed that of PTEN. LY294002 inhibited the biological function of HUVECs through inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/eNOS pathway. In vivo modeling in diabetic rat wounds showed that pioglitazone pretreatment enhanced the therapeutic efficacy of MSCs-derived exosomes and accelerated diabetic wound healing via enhanced angiogenesis. In addition, PGZ-Exos promoted collagen deposition, ECM remodeling and VEGF and CD31 expression, indicating adequate angiogenesis in diabetic wound healing.
Conclusions: PGZ-Exos accelerated diabetic wound healing by promoting the angiogenic function of HUVECs through activation of the PI3K/AKT/eNOS pathway. This offers a promising novel cell-free therapy for treating diabetic wound healing.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Diabetic wound; Exosomes; Mesenchymal stem cells; Pioglitazone.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang M, Wang C, Chen M, Xi Y, Cheng W, Mao C, Xu T, Zhang X, Lin C, Gao W, Guo Y, Lei B. Efficient angiogenesis-based diabetic wound healing/skin reconstruction through bioactive antibacterial adhesive ultraviolet shielding nanodressing with exosome release. ACS Nano. 2019;13:10279–93. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b03656. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

