Oncogenic KRAS engages an RSK1/NF1 pathway to inhibit wild-type RAS signaling in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 34021083
- PMCID: PMC8166058
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2016904118
Oncogenic KRAS engages an RSK1/NF1 pathway to inhibit wild-type RAS signaling in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
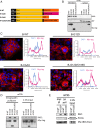
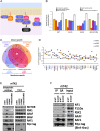
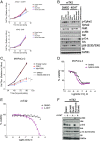
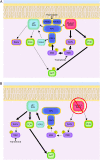
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a lethal malignancy with limited treatment options. Although activating mutations of the KRAS GTPase are the predominant dependency present in >90% of PDAC patients, targeting KRAS mutants directly has been challenging in PDAC. Similarly, strategies targeting known KRAS downstream effectors have had limited clinical success due to feedback mechanisms, alternate pathways, and dose-limiting toxicities in normal tissues. Therefore, identifying additional functionally relevant KRAS interactions in PDAC may allow for a better understanding of feedback mechanisms and unveil potential therapeutic targets. Here, we used proximity labeling to identify protein interactors of active KRAS in PDAC cells. We expressed fusions of wild-type (WT) (BirA-KRAS4B), mutant (BirA-KRAS4BG12D), and nontransforming cytosolic double mutant (BirA-KRAS4BG12D/C185S) KRAS with the BirA biotin ligase in murine PDAC cells. Mass spectrometry analysis revealed that RSK1 selectively interacts with membrane-bound KRASG12D, and we demonstrate that this interaction requires NF1 and SPRED2. We find that membrane RSK1 mediates negative feedback on WT RAS signaling and impedes the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells upon the ablation of mutant KRAS. Our findings link NF1 to the membrane-localized functions of RSK1 and highlight a role for WT RAS signaling in promoting adaptive resistance to mutant KRAS-specific inhibitors in PDAC.
Keywords: BioID; KRAS; NF1; PDAC; RSK.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: D.A.T. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board and receives stock options from Leap Therapeutics, Surface Oncology, and Cygnal Therapeutics. D.A.T. is cofounder of Mestag Therapeutics. D.A.T. receives grant funding from the Lustgarten Foundation. D.A.T. has received Sponsored Research Agreements from Fibrogen, Mestag, and ONO Therapeutics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NF1 loss of function as an alternative initiating event in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Cell Rep. 2022 Nov 8;41(6):111623. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111623. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36351408 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic ERBB2 aberrations and KRAS mutations cooperate to promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression.Carcinogenesis. 2020 Mar 13;41(1):44-55. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz086. Carcinogenesis. 2020. PMID: 31046123
-
Loss of Somatostatin Receptor Subtype 2 Promotes Growth of KRAS-Induced Pancreatic Tumors in Mice by Activating PI3K Signaling and Overexpression of CXCL16.Gastroenterology. 2015 Jun;148(7):1452-65. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.02.009. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 25683115
-
Anticipating resistance to KRAS inhibition: a novel role for USP21 in macropinocytosis regulation.Genes Dev. 2021 Oct 1;35(19-20):1325-1326. doi: 10.1101/gad.348971.121. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 34599002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting KRAS for the potential treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Recent advancements provide hope (Review).Oncol Rep. 2023 Nov;50(5):206. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8643. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37800636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oncogenic mutations of KRAS modulate its turnover by the CUL3/LZTR1 E3 ligase complex.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Mar 7;7(5):e202302245. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302245. Print 2024 May. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 38453365 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative splicing and related RNA binding proteins in human health and disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Feb 2;9(1):26. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01734-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38302461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct GDP-KRASG12C inhibitors and mechanisms of resistance: the tip of the iceberg.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023 Mar 16;15:17588359231160141. doi: 10.1177/17588359231160141. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36950276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ACAGT-007a, an ERK MAPK Signaling Modulator, in Combination with AKT Signaling Inhibition Induces Apoptosis in KRAS Mutant Pancreatic Cancer T3M4 and MIA-Pa-Ca-2 Cells.Cells. 2022 Feb 17;11(4):702. doi: 10.3390/cells11040702. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35203351 Free PMC article.
-
SPRED2 Is a Novel Regulator of Autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells and Normal Hepatocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 6;25(11):6269. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116269. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and Results End (SEER) Program (https://seer.cancer.gov/) SEER*Stat Database: Incidence - SEER Research Data, 9 Registries, Nov 2020 Sub (1975–2018) - Linked To County Attributes - Time Dependent (1990–2018) Income/Rurality, 1969–2019 Counties, National Cancer Institute, DCCPS, Surveillance Research Program, released April 2021, based on the November 2020 submission.
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer , WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2019. 5th ed. In: Tumours of the pancreas. World Health Organization, 295–370 (2019).
-
- Manzano H., et al. ., Clinical benefit with gemcitabine (GEM) as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer (APC). Ann. Oncol. 9, 54 (1998).
-
- King R. S., Gemcitabine. New first-line therapy for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Pract. 4, 353–354 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

