Fluorescence Fluctuation Spectroscopy enables quantification of potassium channel subunit dynamics and stoichiometry
- PMID: 34021177
- PMCID: PMC8140153
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90002-2
Fluorescence Fluctuation Spectroscopy enables quantification of potassium channel subunit dynamics and stoichiometry
Abstract
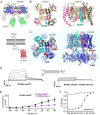
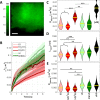
Voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels are a family of membrane proteins that facilitate K+ ion diffusion across the plasma membrane, regulating both resting and action potentials. Kv channels comprise four pore-forming α subunits, each with a voltage sensing domain, and they are regulated by interaction with β subunits such as those belonging to the KCNE family. Here we conducted a comprehensive biophysical characterization of stoichiometry and protein diffusion across the plasma membrane of the epithelial KCNQ1-KCNE2 complex, combining total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy and a series of complementary Fluorescence Fluctuation Spectroscopy (FFS) techniques. Using this approach, we found that KCNQ1-KCNE2 has a predominant 4:4 stoichiometry, while non-bound KCNE2 subunits are mostly present as dimers in the plasma membrane. At the same time, we identified unique spatio-temporal diffusion modalities and nano-environment organization for each channel subunit. These findings improve our understanding of KCNQ1-KCNE2 channel function and suggest strategies for elucidating the subunit stoichiometry and forces directing localization and diffusion of ion channel complexes in general.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

