Using the adherence-efficacy relationship of emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate to calculate background hiv incidence: a secondary analysis of a randomized, controlled trial
- PMID: 34021709
- PMCID: PMC8140182
- DOI: 10.1002/jia2.25744
Using the adherence-efficacy relationship of emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate to calculate background hiv incidence: a secondary analysis of a randomized, controlled trial
Abstract
Introduction: Randomized trials of new agents for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) compare against emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (F/TDF), without a placebo group. We used the well-characterized adherence-efficacy relationship for F/TDF to back-calculate the (non-PrEP) counterfactual background HIV incidence (bHIV) in a randomized trial of a novel PrEP agent and estimate comparative efficacy (to counterfactual bHIV).
Methods: The DISCOVER trial (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02842086) randomized 5387 men who have sex with men (MSM) and transgender women who have sex with men and demonstrated non-inferiority of emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide (F/TAF) to F/TDF (HIV incidence rate ratio [IRR] 0·47, 95% CI: 0·19 to 1.15). Tenofovir diphosphate (TFV-DP) levels in dried blood spots (DBS) were assessed for all diagnosed with HIV and in a random 10% of the cohort. We used a Bayesian model with a diffuse prior distribution, derived from established data relating tenofovir diphosphate levels to HIV prevention efficacy. This prior, combined with the F/TDF seroconversion rate and tenofovir diphosphate levels in DISCOVER, yielded Bayesian inferences on the counterfactual bHIV.
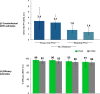
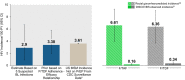
Results: There were six versus 11 postbaseline HIV infections (0.14 vs. 0.25/100 person-years [PY]) on F/TAF and F/TDF respectively. Of the 11 on F/TDF, 10 had low, none had medium and one had high tenofovir diphosphate levels; among HIV-negative controls, 5% of the person-time years had low, 9% had medium and 86% had high TFV-DP levels. A non-informative prior distribution for counterfactual bHIV, combined with the prior for TFV-DP level-efficacy relationship, yielded a posterior counterfactual bHIV of 3·4 infections/100 PY (0.80 Bayesian credible interval [CrI] 1·9 to 5·9), which suggests a median HIV efficacy of 96% (0.95 CrI [88% to 99%]) for F/TAF and 93% (0.95 CrI [87% to 96%]) for F/TDF compared to bHIV.
Conclusions: Based on the established connection of drug concentrations to PrEP prevention efficacy, a Bayesian framework can be used to estimate a synthetic non-PrEP control group in randomized, active-controlled PrEP trials that include a F/TDF-comparator group.
Keywords: Bayesian inference; PrEP; clinical trial design; counterfactual; tenofovir alafenamide; tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of the International AIDS Society published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the International AIDS Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide vs emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (DISCOVER): primary results from a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, active-controlled, phase 3, non-inferiority trial.Lancet. 2020 Jul 25;396(10246):239-254. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31065-5. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32711800 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Exploring potential drug-drug interactions between masculinizing hormone therapy and oral pre-exposure prophylaxis (F/TDF and F/TAF) among transgender men (iMACT study): a randomized, open-label pharmacokinetic study in Thailand.J Int AIDS Soc. 2025 Apr;28(4):e26445. doi: 10.1002/jia2.26445. J Int AIDS Soc. 2025. PMID: 40195242 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
HIV Preexposure Prophylaxis With Emtricitabine and Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Among Cisgender Women.JAMA. 2024 Mar 19;331(11):930-937. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.0464. JAMA. 2024. PMID: 38427359 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence and HIV Protection Thresholds for Emtricitabine and Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Preexposure Prophylaxis among Cisgender Women: A Systematic Review.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2024 Oct;21(5):264-281. doi: 10.1007/s11904-024-00705-0. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2024. PMID: 39120667
-
Preexposure Prophylaxis for the Prevention of HIV: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force.JAMA. 2023 Aug 22;330(8):746-763. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.9865. JAMA. 2023. PMID: 37606667
Cited by
-
Study design approaches for future active-controlled HIV prevention trials.Stat Commun Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 22;15(1):20230002. doi: 10.1515/scid-2023-0002. eCollection 2024 Jan. Stat Commun Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38250627 Free PMC article.
-
Control groups for HIV prevention efficacy trials: what does the future hold?Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2023 Nov 1;18(6):349-356. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000818. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2023. PMID: 37712852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Counterfactual estimation of efficacy against placebo for novel PrEP agents using external trial data: example of injectable cabotegravir and oral PrEP in women.J Int AIDS Soc. 2023 Jun;26(6):e26118. doi: 10.1002/jia2.26118. J Int AIDS Soc. 2023. PMID: 37363917 Free PMC article.
-
HIV Prevention Among Men Who Have Sex With Men: Tenofovir Alafenamide Combination Preexposure Prophylaxis Versus Placebo.J Infect Dis. 2024 Apr 12;229(4):1123-1130. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad507. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 37969014 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy estimates of oral pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention in cisgender women with partial adherence.Nat Med. 2023 Nov;29(11):2748-2752. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02564-5. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Nat Med. 2023. PMID: 37798438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Molina JM, Capitant C, Spire B, Pialoux G, Cotte L, Charreau I, et al. On‐demand preexposure prophylaxis in men at high risk for HIV‐1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2237–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

