Downregulation of CD151 restricts VCAM-1 mediated leukocyte infiltration to reduce neurobiological injuries after experimental stroke
- PMID: 34022890
- PMCID: PMC8140507
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-021-02171-6
Downregulation of CD151 restricts VCAM-1 mediated leukocyte infiltration to reduce neurobiological injuries after experimental stroke
Abstract
Background: Translational failures in anti-adhesion molecule therapies after stroke reveal the necessity of developing new strategies that not only interrupt leukocyte recruitment but also consider the inhibition of endothelial cell inflammation, verification of therapeutic time window, and normal function maintenance of circulating leukocytes. Our study focused on the potential therapeutic value of CD151 downregulation in improving current anti-adhesion molecule therapies.
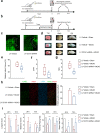
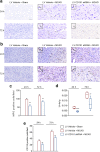
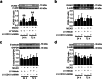
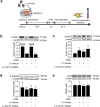
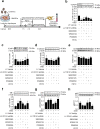
Methods: Lentivirus intracerebroventricular administration was conducted to inhibit the CD151 expression and observe its functional influence on neurological injuries and outcomes. Then, immunohistochemistry and myeloperoxidase activity assessment were performed to explore the effects of CD151 expression on neutrophil and monocyte recruitment after rat cerebral ischemia. Primary rat brain microvascular endothelial cells were subjected to oxygen glucose deprivation and reoxygenation to elucidate the underlying working mechanisms between CD151 and VCAM-1.
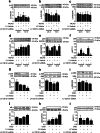
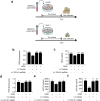
Results: The CD151 downregulation remarkably reduced neurological injuries and improved neurological outcomes, which were accompanied with reduced neutrophil and monocyte infiltration after the CD151 downregulation. The VCAM-1 expression was remarkably decreased among the adhesion molecules on the endothelial cell responsible for neutrophil and monocyte infiltration. The activation of p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways was restricted after the CD151 downregulation. p38 MAPK and NF-κB inhibitors decreased the VCAM-1 expression, and p38 acted as an upstream regulator of NF-κB. However, CD151 downregulation did not directly influence the neutrophil and monocyte activation.
Conclusions: Overall, CD151 regulated the expression of adhesion molecules. It also played a critical role in suppressing VCAM-1-mediated neutrophil and monocyte infiltration via the p38/NF-κB pathway. This study possibly provided a new basis for improving current anti-adhesion molecule therapies.
Keywords: CD151; Endothelial cell; Monocyte; Neutrophil; Stroke; VCAM-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Visfatin Promotes Monocyte Adhesion by Upregulating ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 Expression in Endothelial Cells via Activation of p38-PI3K-Akt Signaling and Subsequent ROS Production and IKK/NF-κB Activation.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(6):1398-1411. doi: 10.33594/000000098. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31075190
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells is regulated by PI 3-kinase/Akt/MAPK/NF-kappaB: inhibitory role of curcumin.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):G259-68. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00087.2009. Epub 2009 Jun 11. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19520742 Free PMC article.
-
Chrysin Attenuates VCAM-1 Expression and Monocyte Adhesion in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Brain Endothelial Cells by Preventing NF-κB Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 3;18(7):1424. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071424. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28671640 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression and signaling during disease: regulation by reactive oxygen species and antioxidants.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Sep 15;15(6):1607-38. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3522. Epub 2011 May 11. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011. PMID: 21050132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen peroxide activation of endothelial cell-associated MMPs during VCAM-1-dependent leukocyte migration.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2006 Dec 31;52(4):8-16. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2006. PMID: 17543193 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: A Therapeutic Target for Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 May 6;15:847440. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.847440. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35600078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative regulation of angiogenesis and the MAPK pathway may be a shared biological pathway between IS and epilepsy.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 4;18(10):e0286426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286426. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37792772 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of Arg1-Positive Microglia/Macrophages Exacerbates Cerebral Ischemic Damage by Facilitating the Inflammatory Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 27;23(21):13055. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113055. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361836 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs Associated with Parenchymal Hematoma After Endovascular Mechanical Reperfusion for Acute Ischemic Stroke in Rats.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 12;13(2):449. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020449. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002863 Free PMC article.
-
sVCAM1 in the Hippocampus Contributes to Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction in Mice by Inducing Microglial Activation Through the VLA-4 Receptor.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Sep;59(9):5485-5503. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02924-1. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35727436
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

