The impact of exercise interventions concerning executive functions of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34022908
- PMCID: PMC8141166
- DOI: 10.1186/s12966-021-01135-6
The impact of exercise interventions concerning executive functions of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Previous studies found that exercise interventions have positive effects on executive functions of the general population. However, studies seldom target executive functions of children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). This study aimed to synthesise empirical studies regarding the effects of exercise interventions on executive functions of children and adolescents with ADHD.
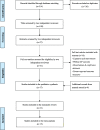
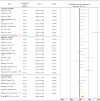
Methods: A systematic search of the relevant literature was conducted in March 2020 through six electronic databases: CINAHL Complete, Eric, MEDLINE, PsychINFO, SPORTDiscus with Full Text, and Web of Science. Randomised controlled trials/quasi-experimental designs that applied exercise interventions and assessed executive functions through neurocognitive tasks among children and adolescents with ADHD were included. Altogether, 314 studies were identified, from which 31 full texts were independently assessed by two authors for eligibility. Finally, 21 studies underwent systematic reviews and 15 were selected for meta-analysis. Data extraction procedures and risk of bias analysis were conducted by two independent authors using the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) scale.
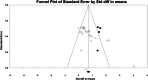
Results: The findings indicated that exercise interventions improved overall executive functions of children and adolescents with ADHD (SMD = 0.611, 95% CI [0.386 to 0.836], p < 0.01). Exercise interventions had a moderate-to-large positive effect on inhibitory control (g = 0.761, 95% CI [0.376 to 1.146], p < 0.01) and cognitive flexibility (g = 0.780, 95% CI [0.331 to 1.228], p < 0.001). Likewise, during the subgroup analysis, intervention intensity and sessions of exercise (acute vs chronic) significantly moderated exercise intervention rather than intervention type.
Conclusions: Chronic sessions of exercise interventions with moderate intensity should be incorporated as treatment for children with ADHD to promote executive functions.
Keywords: ADHD; Children and adolescents; Executive functions; Physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of non-pharmacological interventions on executive functions in children and adolescents with ADHD: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Asian J Psychiatr. 2023 Sep;87:103692. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2023.103692. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Asian J Psychiatr. 2023. PMID: 37450981
-
The Effects of Exercise Interventions on Executive Functions in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2022 Jan;52(1):75-88. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01545-3. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 34468951
-
Comparative effectiveness of physical activity interventions on cognitive functions in children and adolescents with Neurodevelopmental Disorders: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2025 Jan 13;22(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12966-024-01702-7. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2025. PMID: 39806448 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of physical activity interventions on executive functions in school-age children with ADHD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Affect Disord. 2025 Jun 1;378:175-190. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2025.01.155. Epub 2025 Feb 25. J Affect Disord. 2025. PMID: 40010649
-
Effect of aerobic exercise on the improvement of executive function in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Psychol. 2024 Jun 4;15:1376354. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1376354. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38952825 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The impact of the physical activity intervention on sleep in children and adolescents with neurodevelopmental disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Aug 13;15:1438786. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1438786. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39193141 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Activity and Executive Function in Children With ADHD: The Mediating Role of Sleep.Front Pediatr. 2022 Jan 20;9:775589. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.775589. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35127588 Free PMC article.
-
Be Divergent, Be Green! The Moderating Role of Gender in the Association Between Divergent Thinking and Pro-Environmental Behaviours in Children.Children (Basel). 2024 Dec 8;11(12):1497. doi: 10.3390/children11121497. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39767926 Free PMC article.
-
Intervention effect of a single exercise session on executive function in children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a three-level meta-analysis.BMC Pediatr. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):519. doi: 10.1186/s12887-025-05846-8. BMC Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40604676 Free PMC article.
-
Toward Precision Medicine in ADHD.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jul 6;16:900981. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.900981. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35874653 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Association AP . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5 (DSM-5®) Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Pub; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical