Developmental basis of trachea-esophageal birth defects
- PMID: 34023332
- PMCID: PMC8277759
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.05.015
Developmental basis of trachea-esophageal birth defects
Abstract
Trachea-esophageal defects (TEDs), including esophageal atresia (EA), tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF), and laryngeal-tracheoesophageal clefts (LTEC), are a spectrum of life-threatening congenital anomalies in which the trachea and esophagus do not form properly. Up until recently, the developmental basis of these conditions and how the trachea and esophagus arise from a common fetal foregut was poorly understood. However, with significant advances in human genetics, organoids, and animal models, and integrating single cell genomics with high resolution imaging, we are revealing the molecular and cellular mechanisms that orchestrate tracheoesophageal morphogenesis and how disruption in these processes leads to birth defects. Here we review the current understanding of the genetic and developmental basis of TEDs. We suggest future opportunities for integrating developmental mechanisms elucidated from animals and organoids with human genetics and clinical data to gain insight into the genotype-phenotype basis of these heterogeneous birth defects. Finally, we envision how this will enhance diagnosis, improve treatment, and perhaps one day, lead to new tissue replacement therapy.
Keywords: Congenital anomalies; Development; EA/TEF; Esophageal atresia; Esophagus; Foregut; Laryngotracheoesophageal cleft; Trachea; Tracheoesophageal fistula.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
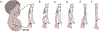
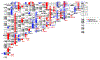


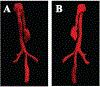
References
-
- Arrington CB, Patel A, Bacino CA, Bowles NE, 2010. Haploinsufficiency of the LIM domain containing preferred translocation partner in lipoma (LPP) gene in patients with tetralogy of Fallot and VACTERL association. Am J Med Genet A 152A, 2919–2923. - PubMed
-
- Bachiller D, Klingensmith J, Kemp C, Belo JA, Anderson RM, May SR, McMahon JA, McMahon AP, Harland RM, Rossant J, De Robertis EM, 2000. The organizer factors Chordin and Noggin are required for mouse forebrain development. Nature 403, 658–661. - PubMed
-
- Bachiller D, Klingensmith J, Shneyder N, Tran U, Anderson R, Rossant J, De Robertis EM, 2003. The role of chordin/Bmp signals in mammalian pharyngeal development and DiGeorge syndrome. Development 130, 3567–3578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

