SARS-CoV-2 mutations, vaccines, and immunity: implication of variants of concern
- PMID: 34023862
- PMCID: PMC8140323
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00623-2
SARS-CoV-2 mutations, vaccines, and immunity: implication of variants of concern
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
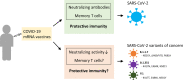
Comment on
-
mRNA vaccine-elicited antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and circulating variants.Nature. 2021 Apr;592(7855):616-622. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03324-6. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33567448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tarke, A. et al. Negligible impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants on CD4+and CD8+ T cell reactivity in COVID-19 exposed donors and vaccinees. Preprint at bioRxiv10.1101/2021.02.27.433180 (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

