A comprehensive review of m6A/m6Am RNA methyltransferase structures
- PMID: 34023900
- PMCID: PMC8287941
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab378
A comprehensive review of m6A/m6Am RNA methyltransferase structures
Abstract
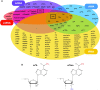
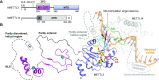
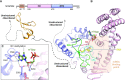
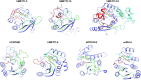
Gene expression is regulated at many levels including co- or post-transcriptionally, where chemical modifications are added to RNA on riboses and bases. Expression control via RNA modifications has been termed 'epitranscriptomics' to keep with the related 'epigenomics' for DNA modification. One such RNA modification is the N6-methylation found on adenosine (m6A) and 2'-O-methyladenosine (m6Am) in most types of RNA. The N6-methylation can affect the fold, stability, degradation and cellular interaction(s) of the modified RNA, implicating it in processes such as splicing, translation, export and decay. The multiple roles played by this modification explains why m6A misregulation is connected to multiple human cancers. The m6A/m6Am writer enzymes are RNA methyltransferases (MTases). Structures are available for functionally characterized m6A RNA MTases from human (m6A mRNA, m6A snRNA, m6A rRNA and m6Am mRNA MTases), zebrafish (m6Am mRNA MTase) and bacteria (m6A rRNA MTase). For each of these MTases, we describe their overall domain organization, the active site architecture and the substrate binding. We identify areas that remain to be investigated, propose yet unexplored routes for structural characterization of MTase:substrate complexes, and highlight common structural elements that should be described for future m6A/m6Am RNA MTase structures.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




References
-
- Wei C., Gershowitz A., Moss B.. N6, O2′-dimethyladenosine a novel methylated ribonucleoside next to the 5′ terminal of animal cell and virus mRNAs. Nature. 1975; 257:251–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

