Fabrication and Performance of a Multi-Discharge Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Array
- PMID: 34024956
- PMCID: PMC8132946
- DOI: 10.1109/TPS.2021.3064993
Fabrication and Performance of a Multi-Discharge Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Array
Abstract
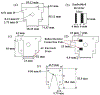
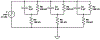
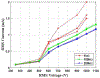
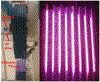
Cold atmospheric pressure plasma (CAP) has been shown to kill bacteria and remove biofilms. Here we report the development of a unique CAP array device consisting of a parallel stack of eight linear-discharge plasma elements that create a ~ 5 cm2 (2.4 cm × 2 cm) treatment area. The CAP device is fabricated from Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramic (LTCC) layers to create 24 mm long linear-discharge channels (500 μm gap) with embedded opposing silver metal electrodes. A 20 kHz AC voltage (0.5-5 kV) applied to the electrodes generates an Ar/O2 plasma between the plates, with the gas flow directing the reactive species toward the biological sample (biofilms, etc.) to affect the antimicrobial treatment. External ballast resistors were used to study discharge uniformity in the stacked array elements and internal thick film ballast resistors (≈150 kΩ) were developed to create a fully integrated device. Typical element discharge currents were 1-2.5 mA with the total array current tested at 20 mA to provide optimal device uniformity. The plasma discharge was further shown to produce reactive hydrogen peroxide and exert antimicrobial effects on Pseudomonas biofilms and Salmonella contaminated eggshell samples, with >99% of the bacterial cells killed with less than 60 seconds of plasma exposure.
Keywords: Cold atmospheric pressure plasma; antimicrobial; biofilms; reactive oxygen species.
Figures


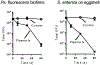
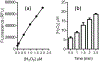
References
-
- Percival SL, Suleman L, Vuotto C, and Donelli G, “Healthcare-associated infections, medical devices and biofilms: risk, tolerance and control,” Journal of Medical Microbiology, vol. 64, pp. 323–334, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Kong MG, Kroesen G, Morfill G, Nosenko T, Shimizu T, Dijk JV, and Zimmermann JL, “Plasma medicine: an introductory review,” New Journal of Physics, vol. 11, no. 11, p. 115012, 2009.
-
- Kumar H, Franzetti L, Kaushal A, and Kumar D, “Pseudomonas fluorescens: a potential food spoiler and challenges and advances in its detection,” Annals of Microbiology, vol. 69, pp. 873–883, 2019.
-
- Graves DB, “The emerging role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in redox biology and some implications for plasma applications to medicine and biology,” Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, vol. 45, p. 263001, 2012.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
