Screening of Anti-Lipase Components of Artemisia argyi Leaves Based on Spectrum-Effect Relationships and HPLC-MS/MS
- PMID: 34025435
- PMCID: PMC8138579
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.675396
Screening of Anti-Lipase Components of Artemisia argyi Leaves Based on Spectrum-Effect Relationships and HPLC-MS/MS
Abstract
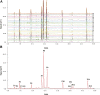
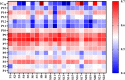
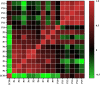
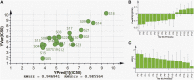
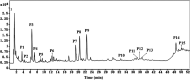
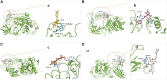
Pancreatic lipase is a key lipase for triacylglyceride digestion and absorption, which is recognized as a promising target for treatment of metabolic disorders. Natural phytochemicals are hopeful sources for pancreatic lipase inhibitors. The leaves of Artemisia argyi H.Lév. and Vaniot (AL) is commonly used as herbal medicine or food supplement in China and other Asian countries for hundreds of years. AL mainly contains essential oils, phenolic acids, flavonoids and terpenoids, which exhibit many pharmacological activities such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, analgetic, anti-cancer, anti-diabetes and immunomodulatory effects. However, the anti-lipase activity of AL was lack of study and the investigation of anti-lipase ingredients from AL was also insufficient. In the present study, the anti-lipase activity of AL was evaluated in vitro and the potentially pancreatic lipase inhibitors of AL were investigated. High performance liquid chromatography was used to establish fingerprints of AL samples, and fifteen peaks were selected. The anti-lipase activities of AL samples were evaluated by a pancreatic lipase inhibition assay. Then, the spectrum-effect relationships between fingerprints and pancreatic lipase inhibitory activities were investigated to identify the anti-lipase constitutes in AL. As the results, four caffeoylquinic acids, which were identified as neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, isochlorogenic acid B, and isochlorogenic acid A by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry, were selected as potential pancreatic lipase inhibitors in AL. Moreover, anti-lipase activity assessment and molecular docking study of the four compounds were performed to validate the potential lipase inhibitors in AL. The results revealed that the four caffeoylquinic acids in AL as bioactive compounds displayed with anti-lipase activity. The present research provided evidences for the anti-lipase activity of AL, and suggested that some bioactive compounds in AL could be used as lead compounds for discovering of new pancreatic lipase inhibitors.
Keywords: Artemisia argyi leaves; HPLC-MS/MS; anti-lipase activity; pancreatic lipase; spectrum-effect relationships.
Copyright © 2021 Chang, Zhang, Yang, Zheng and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
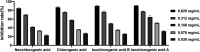
Similar articles
-
Characterization of phenolics and discovery of α-glucosidase inhibitors in Artemisia argyi leaves based on ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and relevance analysis.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022 Oct 25;220:114982. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114982. Epub 2022 Aug 4. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022. PMID: 35944337
-
Screening Anti-Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis Effective Ingredients of Total Flavonoid From Artemisia argyi Folium Based on Spectrum-Effect Relationship.Phytochem Anal. 2025 Jun;36(4):943-956. doi: 10.1002/pca.3479. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Phytochem Anal. 2025. PMID: 39532485
-
[Comparison of chemical components between Artemisia stolonifera and Artemisia argyi using UPLC-Q-TOF-MS].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Sep;45(17):4057-4064. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200602.203. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33164389 Chinese.
-
From longevity grass to contemporary soft gold: Explore the chemical constituents, pharmacology, and toxicology of Artemisia argyi H.Lév. & vaniot essential oil.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114404. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114404. Epub 2021 Jul 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34246739 Review.
-
Inhibitors of pancreatic lipase: state of the art and clinical perspectives.EXCLI J. 2014 Aug 22;13:897-921. eCollection 2014. EXCLI J. 2014. PMID: 26417311 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Caffeic Acid, an Allelochemical in Artemisia argyi, Inhibits Weed Growth via Suppression of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway and the Biosynthesis of Gibberellin and Phytoalexin.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jan 6;12:802198. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.802198. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35069660 Free PMC article.
-
A multicenter analysis on the changes of sIgE in China during the early period of COVID-19 pandemic.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Nov;11(11):e1072. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1072. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 38018584 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Screening of Lipase Inhibitors from Ophiopogonis Radix Using High-Performance Thin Layer Chromatography by Two Step Gradient Elution Combined with Bioautographic Method.Molecules. 2022 Feb 9;27(4):1155. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041155. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35208944 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrum-Effect Relationships as an Effective Approach for Quality Control of Natural Products: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Oct 10;28(20):7011. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207011. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37894489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autofluorescence and Metabotyping of Soybean Varieties Using Confocal Laser Microscopy and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometric Approaches.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jun 30;14(13):1995. doi: 10.3390/plants14131995. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40648004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eswaramoorthy R., Hailekiros H., Kedir F., Endale M. (2021). In Silico Molecular Docking, DFT Analysis and ADMET Studies of Carbazole Alkaloid and Coumarins from Roots of Clausena Anisata: A Potent Inhibitor for Quorum Sensing. Adv. Appl. Bioinform. Chem. 14, 13–24. 10.2147/AABC.S290912 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

