Gut Microbiota Changes in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder Treated With Vortioxetine
- PMID: 34025474
- PMCID: PMC8138160
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.641491
Gut Microbiota Changes in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder Treated With Vortioxetine
Abstract
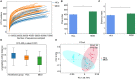
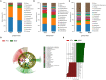
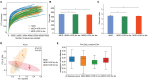
Vortioxetine hydrobromide is a common clinical medication for major depressive disorder (MDD). However, it remains unclear whether vortioxetine hydrobromide acts by affecting the structure and composition of gut microbiota. Here, we analyzed fecal samples from 28 healthy controls (HCs) and 26 patients with MDD before treatment with vortioxetine hydrobromide, at 4 weeks after treatment, and at 8 weeks after treatment. High-throughput pyrosequencing showed that, according to the Chao1 and Shannon indices, fecal bacterial α-diversity was higher in the patients with MDD than in the HCs (p < 0.05), but no significant differences were observed after vortioxetine hydrobromide treatment (p > 0.05). PCoA results revealed that the gut microbiota composition was significantly different between the MDD groups and HCs. Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria were strongly increased, whereas Firmicutes were significantly reduced in the MDD group compared with the HCs. After treatment with vortioxetine hydrobromide, Firmicutes were significantly increased, and the proportion of Bacteroidetes decreased. Most notably, Lachnospira, Roseburia, and Faecalibacterium were negatively correlated with the severity of depressive symptoms. Taken together, our data indicate changes in the fecal microbiota composition in MDD patients compared with HCs, and vortioxetine hydrobromide may treat MDD through regulation of the gut microflora.
Keywords: gut microbiota; gut-brain axis; major depression disorder; treatment; vortioxetine hydrobromide.
Copyright © 2021 Ye, Wang, Zhu, Wang, Li, Tang and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Burrows K, Stewart JL, Antonacci C, Kuplicki R, Thompson K, Taylor A, et al. . Association of poorer dietary quality and higher dietary inflammation with greater symptom severity in depressed individuals with appetite loss. J Affect Disord. (2020) 263:99–106. 10.1016/j.jad.2019.11.160 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

