Effects of Small-Sided Game Interventions on the Technical Execution and Tactical Behaviors of Young and Youth Team Sports Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34025529
- PMCID: PMC8138063
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.667041
Effects of Small-Sided Game Interventions on the Technical Execution and Tactical Behaviors of Young and Youth Team Sports Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
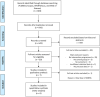
Background: Small-sided games (SSGs) are an adjusted form of official games that are often used in training scenarios to introduce a specific tactical issue to team sports players. Besides the acute effects of SSGs on players' performance, it is expectable that the consistent use of these drill-based games induces adaptations in the technical execution and tactical behaviors of youth team sports players. Objective: This systematic review with meta-analysis was conducted to assess the effects of SSG programs on the technical execution and tactical behaviors of young and youth team sports players. Data Sources: The data sources utilized were PubMed, Scopus, SPORTDiscus, and Web of Science. Study Eligibility Criteria: (i) Young and youth team sports players (i.e., < 18 years old) of any sex or skill level, without injury, illness, or other clinical conditions; (ii) SSGs-based programs not restricted to the duration and a minimum of one weekly training session; (iii) passive or active control groups; (iv) pre-post interventions values of technical execution and/or tactical behavior; (v) randomized and non-randomized controlled trials; and (vi) peer-reviewed original full-text studies written in English, Portuguese and/or Spanish. Results: The database search initially yielded 803 titles. From those, six articles were eligible for the systematic review and meta-analysis. None of the included studies presented tactical behavior outcomes. The results showed a small effect of SSGs on technical execution (ES = 0.59; 95% CI = 0.29 to 0.89; p < 0.001; I 2 = 0.0%; Egger's test p = 0.590) when compared to controls. Sub-group analysis of the training factor revealed similar (p = 0.433) moderate (ES = 0.68, four study groups) and small (ES = 0.44, three study groups) improvements in technical execution after >17 and <17 SSG training sessions, respectively. Conclusions: This systematic review and meta-analysis revealed a significant beneficial effect of using SSG training programs for enhancing technical execution in young and youth players. The benefits were similar despite the various numbers of training sessions applied. Further studies should add tactical behaviors as one of the outcomes for controlling the effects of SSG training programs.
Keywords: Soccer; athletic performance; decision-making; football; motor skills; youth sports.
Copyright © 2021 Clemente, Ramirez-Campillo, Sarmento, Praça, Afonso, Silva, Rosemann and Knechtle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of Training Programs on Decision-Making in Youth Team Sports Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Psychol. 2021 May 31;12:663867. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.663867. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34135822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Mental Fatigue in Total Running Distance and Tactical Behavior During Small-Sided Games: A Systematic Review With a Meta-Analysis in Youth and Young Adult's Soccer Players.Front Psychol. 2021 Mar 17;12:656445. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.656445. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33815237 Free PMC article.
-
Combining small-sided soccer games and running-based methods: A systematic review.Biol Sport. 2021 Oct;38(4):617-627. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2021.102932. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Biol Sport. 2021. PMID: 34937972 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Recreational Small-Sided Soccer Games on Bone Mineral Density in Untrained Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Apr 13;9(4):457. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9040457. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33924705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of the Small-Sided Soccer Games on Blood Pressure in Untrained Hypertensive Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;9(3):345. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9030345. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803787 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can high-intensity interval training and small-sided games be effective for improving physical fitness after detraining? A parallel study design in youth male soccer players.PeerJ. 2022 Jul 1;10:e13514. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13514. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35795177 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Leveling The Playing Field in Youth Basketball: How Compensatory Training With Small-Sided Games Enhances Physical Fitness and Reduces Relative Age Effect Bias in Match Selection.J Sports Sci Med. 2025 Jun 1;24(2):341-350. doi: 10.52082/jssm.2025.341. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Sports Sci Med. 2025. PMID: 40469873 Free PMC article.
-
Special Issue "Sports Science in Children".Children (Basel). 2024 Feb 5;11(2):202. doi: 10.3390/children11020202. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397315 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of implicit vs. explicit Instructions on tactical performance in under-20 soccer players.Front Sports Act Living. 2024 Sep 9;6:1441125. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1441125. eCollection 2024. Front Sports Act Living. 2024. PMID: 39346493 Free PMC article.
-
Space and players' number constrains the external and internal load demands in youth futsal.Front Sports Act Living. 2024 May 28;6:1376024. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1376024. eCollection 2024. Front Sports Act Living. 2024. PMID: 38863569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arslan E., Orer G., Clemente F. (2020). Running-based high-intensity interval training vs. small-sided game training programs: effects on the physical performance, psychophysiological responses and technical skills in young soccer players. Biol. Sport 37, 165–173. 10.5114/biolsport.2020.94237 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bredt S. G. T., Praça G. M., Figueiredo L. S., de Paula L. V., Silva P. C. R., de Andrade A. G. P., et al. . (2016). Reliability of physical, physiological and tactical measures in small-sided soccer games with numerical equality and numerical superiority. Rev. Bras. Cineantropometria & Desempenho Hum. 18:602–10. 10.5007/1980-0037.2016v18n5p602 - DOI
-
- Caso S., van der Kamp J. (2020). Variability and creativity in small-sided conditioned games among elite soccer players. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 48:101645. 10.1016/j.psychsport.2019.101645 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

