Risk Factors of Hypoperfusion on MRI of Ischemic Stroke Patients Within 7 Days of Onset
- PMID: 34025571
- PMCID: PMC8137898
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.668360
Risk Factors of Hypoperfusion on MRI of Ischemic Stroke Patients Within 7 Days of Onset
Abstract
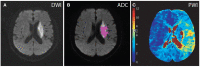
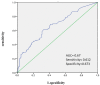
Objective: Hypoperfusion is an important factor determining the prognosis of ischemic stroke patients. The present study aimed to investigate possible predictors of hypoperfusion on MRI of ischemic stroke patients within 7 days of stroke onset. Methods: Ischemic stroke patients, admitted to the comprehensive Stroke Center of Shanghai Fourth People's Hospital affiliated to Tongji University within 7 days of onset between January 2016 and June 2017, were recruited to the present study. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), including both diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI), was performed within 7 days of the symptom onset. Time to maximum of the residue function (T max ) maps were automatically evaluated using the RAPID software. The volume of hypoperfusion was measured outside the infarct area based on ADC < 620 × 10-6 mm2/s. The 90 d mRS score was assessed through either clinic visits or telephone calls. Multivariate step-wise analysis was used to assess the correlation between MR findings and clinical variables, including the demographic information, cardio-metabolic characteristics, and functional outcomes. Results: Among 635 patients admitted due to acute ischemic stroke within 7 days of onset, 241 met the inclusion criteria. Hypoperfusion volume of 38 ml was the best cut-off value for predicting poor prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction (90 d-mRS score ≥ 2). The incidences of MR perfusion T max > 4-6 s maps with a volume of 0-38 mL or >38 mL were 51.9% (125/241) and 48.1% (116/241), respectively. Prior stroke and vascular stenosis (≥70%) were associated with MR hypoperfusion. Multivariate step-wise analysis showed that prior stroke and vascular stenosis (≥70%) were risk factors of T max > 4-6 s maps, and the odds ratios (OR) were 3.418 (adjusted OR 95% CI: 1.537-7.600), and 2.265 (adjusted OR, 95% CI: 1.199-4.278), respectively. Conclusion: Our results suggest that prior stroke and vascular stenosis (≥70%) are strong predictors of hypoperfusion in patients with acute ischemic stroke within 7 days of stroke onset.
Keywords: correlation analysis; ischemic stroke; magnetic resonance imaging; risk factors; time to maximum of the residue function.
Copyright © 2021 Xiao, Liang, Wang, Wang, Wang and Bi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk factors of perfusion and diffusion abnormalities on MRI in hemispheric TIA: a case-control study.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Dec;7(24):808. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.12.69. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 32042824 Free PMC article.
-
History of Hypertension Is Associated With MR Hypoperfusion in Chinese Inpatients With DWI-Negative TIA.Front Neurol. 2019 Aug 14;10:867. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00867. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31474927 Free PMC article.
-
Time-dependent parameter of perfusion imaging as independent predictor of clinical outcome in symptomatic carotid artery stenosis.BMC Neurol. 2016 Apr 19;16:50. doi: 10.1186/s12883-016-0576-5. BMC Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27094741 Free PMC article.
-
The Frequency and Associated Factors of Asymmetrical Prominent Veins: A Predictor of Unfavorable Outcomes in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke.Neural Plast. 2021 Sep 17;2021:9733926. doi: 10.1155/2021/9733926. eCollection 2021. Neural Plast. 2021. PMID: 34567108 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Diffusion-Perfusion Mismatch in Acute Ischemic Stroke with a New Automated Perfusion-Weighted Imaging Software: A Retrospective Study.Neurol Ther. 2022 Dec;11(4):1777-1788. doi: 10.1007/s40120-022-00409-w. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Neurol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36201112 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Focal Hypoperfusion on Baseline Perfusion-Weighted MRI and the Risk of Subsequent Cerebrovascular Events in Patients With TIA.Neurology. 2025 Aug 26;105(4):e213930. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000213930. Epub 2025 Jul 24. Neurology. 2025. PMID: 40706000 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics features of DSC-PWI in time dimension may provide a new chance to identify ischemic stroke.Front Neurol. 2022 Nov 4;13:889090. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.889090. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36408497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saqqur M, Uchino K, Demchuk AM, Molina CA, Garami Z, Calleja S, et al. . Site of arterial occlusion identified by transcranial Doppler predicts the response to intravenous thrombolysis for stroke. Stroke. (2007) 38:948–54. 10.1161/01.STR.0000257304.21967.ba - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

