Heat Shock Protein A6, a Novel HSP70, Is Induced During Enterovirus A71 Infection to Facilitate Internal Ribosomal Entry Site-Mediated Translation
- PMID: 34025620
- PMCID: PMC8137988
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.664955
Heat Shock Protein A6, a Novel HSP70, Is Induced During Enterovirus A71 Infection to Facilitate Internal Ribosomal Entry Site-Mediated Translation
Abstract
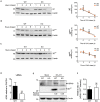
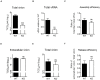
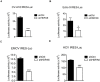
Enterovirus A71 (EV-A71) is a human pathogen causing hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) in children. Its infection can lead to severe neurological diseases or even death in some cases. While being produced in a large quantity during infection, viral proteins often require the assistance from cellular chaperones for proper folding. In this study, we found that heat shock protein A6 (HSPA6), whose function in viral life cycle is scarcely studied, was induced and functioned as a positive regulator for EV-A71 infection. Depletion of HSPA6 led to the reductions of EV-A71 viral proteins, viral RNA and virions as a result of the downregulation of internal ribosomal entry site (IRES)-mediated translation. Unlike other HSP70 isoforms such as HSPA1, HSPA8, and HSPA9, which regulate all phases of the EV-A71 life, HSPA6 was required for the IRES-mediated translation only. Unexpectedly, the importance of HSPA6 in the IRES activity could be observed in the absence of viral proteins, suggesting that HSPA6 facilitated IRES activity through cellular factor(s) instead of viral proteins. Intriguingly, the knockdown of HSPA6 also caused the reduction of luciferase activity driven by the IRES from coxsackievirus A16, echovirus 9, encephalomyocarditis virus, or hepatitis C virus, supporting that HSPA6 may assist the function of a cellular protein generally required for viral IRES activities.
Keywords: HSPA6; enterovirus A71 (EV-A71); induced HSP70; internal ribosomal entry site; viral IRES.
Copyright © 2021 Su, Hwang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Heat Shock Protein 70 Family of Chaperones Regulates All Phases of the Enterovirus A71 Life Cycle.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jul 14;11:1656. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01656. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32760390 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp27 Responds to and Facilitates Enterovirus A71 Replication by Enhancing Viral Internal Ribosome Entry Site-Mediated Translation.J Virol. 2019 Apr 17;93(9):e02322-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02322-18. Print 2019 May 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30814282 Free PMC article.
-
Translocating lipopolysaccharide correlates with the severity of enterovirus A71-induced HFMD by promoting pro-inflammation and viral IRES activity.Gut Pathog. 2021 Nov 22;13(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13099-021-00465-x. Gut Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34809671 Free PMC article.
-
Translation control of Enterovirus A71 gene expression.J Biomed Sci. 2020 Jan 8;27(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0607-9. J Biomed Sci. 2020. PMID: 31910851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is a multivalent hand, foot, and mouth disease vaccine feasible?Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(11):2688-704. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1049780. Epub 2015 May 26. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 26009802 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine Protects Airway Epithelial Cells during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection against Mucin Synthesis, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammatory Response and Inhibits HSPA6 Expression.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2022 Aug 21;2022:4846336. doi: 10.1155/2022/4846336. eCollection 2022. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2022. PMID: 36046596 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Analysis of RNA-Seq Data Identifies Key Gene Signatures and Pathways in Mpox Virus-Induced Gastrointestinal Complications Using Colon Organoid Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 17;25(20):11142. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011142. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456924 Free PMC article.
-
The protein and miRNA profile of plasma extracellular vesicles (EVs) can distinguish feline mammary adenocarcinoma patients from healthy feline controls.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 6;13(1):9178. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36110-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37280313 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Understanding the Mechanism of Cap-Independent Cucurbit Aphid-Borne Yellows Virus Protein Synthesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 18;24(24):17598. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417598. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139425 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Binding Proteins as Regulators of Internal Initiation of Viral mRNA Translation.Viruses. 2022 Jan 19;14(2):188. doi: 10.3390/v14020188. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215780 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Basavappa R., Syed R., Flore O., Icenogle J. P., Filman D. J., Hogle J. M. (1994). Role and mechanism of the maturation cleavage of VP0 in poliovirus assembly: structure of the empty capsid assembly intermediate at 2.9 A resolution. Protein Sci. 3 1651–1669. 10.1002/pro.5560031005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolhassani A., Agi E. (2019). Heat shock proteins in infection. Clin. Chim. Acta 498 90–100. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

