The Associations of Serum IL-37 With the Severity and Prognosis in Patients With Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 34025645
- PMCID: PMC8138168
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636896
The Associations of Serum IL-37 With the Severity and Prognosis in Patients With Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Recent evidences suggested that IL-37 may participate in the pathophysiology of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). Nevertheless, its exact biological role was unknown. The objective of this study was to determine the associations of serum IL-37 with the severity and prognosis in CAP patients based on a retrospective cohort study.
Methods: The whole of 120 healthy subjects and 240 CAP patients were summoned. Peripheral blood was collected and IL-37 was detected using ELISA.
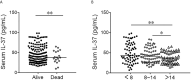
Results: Serum IL-37 was obviously decreased in CAP patients on admission. In addition, serum IL-37 was gradually decreased in parallel with CAP severity scores. Correlative analysis revealed that serum IL-37 was negatively associated with CAP severity scores and inflammatory cytokines. Further logistical regression found that reduction of serum IL-37 augmented the severity of CAP patients. Moreover, the follow-up research was performed in CAP patients. Serum lower IL-37 on admission prolonged the hospital stay in CAP patients. Serum IL-37 combination with PSI and CURB-65 had a stronger predictive capacity for death than IL-37 and CAP severity score alone in CAP patients.
Conclusion: There are remarkably negative correlations between serum IL-37 with the severity and prognosis in CAP patients. Serum IL-37 on admission prolongs the hospital stay, demonstrating that IL-37 may involve in the process of CAP. Serum IL-37 may be regarded as a biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis for CAP patients.
Keywords: IL-37; biomarker; community-acquired pneumonia; community-acquired pneumonia severity score; inflammatory cytokine.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Chen, Xu, Chen, Wang, Liu, Song, Fei, Zhao and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Serum interleukin-17 predicts severity and prognosis in patients with community acquired pneumonia: a prospective cohort study.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Dec 2;21(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01770-6. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 34856971 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Serum Resistin With the Severity and Prognosis in Patients With Community-Acquired Pneumonia.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 9;12:703515. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.703515. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34858392 Free PMC article.
-
Serum IL-27 predicts the severity and prognosis in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: a prospective cohort study.Int J Med Sci. 2022 Jan 1;19(1):74-81. doi: 10.7150/ijms.67028. eCollection 2022. Int J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34975300 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers and clinical scoring systems in community-acquired pneumonia.Ann Thorac Med. 2019 Jul-Sep;14(3):165-172. doi: 10.4103/atm.ATM_305_18. Ann Thorac Med. 2019. PMID: 31333765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers in Community-Acquired Pneumonia (Cardiac and Non-Cardiac).J Clin Med. 2020 Feb 18;9(2):549. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020549. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32085380 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum interleukin-17 predicts severity and prognosis in patients with community acquired pneumonia: a prospective cohort study.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Dec 2;21(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01770-6. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 34856971 Free PMC article.
-
Serum transgelin is a novel prognostic biomarker for COVID-19 patients.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 29;15:1423182. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1423182. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39676863 Free PMC article.
-
Serum TRAIL predicts severity and prognosis in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: a prospective cohort study.Intern Emerg Med. 2022 Nov;17(8):2279-2290. doi: 10.1007/s11739-022-03086-7. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Intern Emerg Med. 2022. PMID: 36241932 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Serum Resistin With the Severity and Prognosis in Patients With Community-Acquired Pneumonia.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 9;12:703515. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.703515. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34858392 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Serum Legumain with Severity and Prognosis Among Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Feb 25;20:437-447. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S507018. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 40027200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han X, Zhou F, Li H, Xing X, Chen L, Wang Y, et al. . Cap-China Network. Effects of Age, Comorbidity and Adherence to Current Antimicrobial Guidelines on Mortality in Hospitalized Elderly Patients With Community-Acquired Pneumonia. BMC Infect Dis (2018) 18:192. 10.1186/s12879-018-3098-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

