Modeling Influencing Factors in B-Cell Reconstitution After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Children
- PMID: 34025685
- PMCID: PMC8138425
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.684147
Modeling Influencing Factors in B-Cell Reconstitution After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Children
Abstract
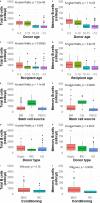
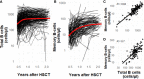
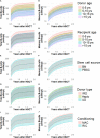
Reduced total and memory B-cell numbers in peripheral blood long term after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) are associated with an increased incidence of infections and immune complications. Using novel modelling strategies, baseline factors influencing B-cell reconstitution can be comprehensively studied. This study aims to investigate the numerical total and memory B-cell reconstitution in children and the association with baseline determinants 0.5-2 years after allogeneic HSCT. Eligible for inclusion were children transplanted in our center between 2004-2017 who received a first HSCT for malignant or non-malignant disorders. The continuous absolute counts of total and memory B-cells were evaluated as outcome measure. Exploratory analysis at one year was done to identify possible determinants. Linear mixed effect modelling was used to analyze the association of these determinants with total and memory B-cell reconstitution 0.5-2 years after HSCT. In a cohort of 223 evaluable patients analyzed at 1-year after HSCT donor age, stem cell source, donor type, recipient age and conditioning were identified as significant determinants for total and memory B-cell numbers. Multivariable analysis revealed that both donor and recipient age were inversely correlated with the size of total and memory B-cell reconstitution. In contrast, no correlation was found with stem cell source, donor type and conditioning. Making use of linear mixed modelling both stem cell donor and recipient age were identified as independent determinants of total and memory B-cell reconstitution 0.5-2 years after HSCT.
Keywords: B lymphocyte; allogeneic; hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; immune reconstitution; linear mixed effect modelling; pediatric.
Copyright © 2021 van der Maas, von Asmuth, Berghuis, van Schouwenburg, Putter, van der Burg and Lankester.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
B Cell Reconstitution and Influencing Factors After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Children.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 12;10:782. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00782. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31031769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Humoral Immune Reconstitution Kinetics after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Children: A Maturation Block of IgM Memory B Cells May Lead to Impaired Antibody Immune Reconstitution.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017 Sep;23(9):1437-1446. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.05.005. Epub 2017 May 8. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28495643
-
Immune Reconstitution and Infection Patterns after Early Alemtuzumab and Reduced Intensity Transplantation for Nonmalignant Disorders in Pediatric Patients.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019 Mar;25(3):556-561. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.10.008. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30321596 Clinical Trial.
-
Immune recovery after in vivo T-cell depletion myeloablative conditioning hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in severe beta-thalassemia children.Eur J Haematol. 2019 Oct;103(4):342-350. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13289. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Eur J Haematol. 2019. PMID: 31276236
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
Cited by
-
The Composite Immune Risk Score predicts overall survival after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A retrospective analysis of 1838 cases.Am J Hematol. 2023 Feb;98(2):309-321. doi: 10.1002/ajh.26792. Epub 2023 Jan 2. Am J Hematol. 2023. PMID: 36591789 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of long- and short-term hematopoietic stem cell ratio causes myeloid-biased hematopoiesis.Elife. 2025 Aug 27;13:RP95880. doi: 10.7554/eLife.95880. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40864176 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: Persistent hypogammaglobulinemia and mixed chimerism after HLA class-II disparate-hematopoietic stem cell transplant.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 9;15:1397567. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1397567. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39044816 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Reconstitution in Pediatric Aplastic Anemia after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-cell Transplantation.Int J Med Sci. 2022 May 1;19(5):821-828. doi: 10.7150/ijms.70146. eCollection 2022. Int J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35693743 Free PMC article.
-
Differential analysis of immune reconstitution after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome and chronic granulomatous disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 14;14:1202772. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1202772. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37388746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Azim H, Elshoury A, Mahadeo KM, Parkman R, Kapoor N. Humoral Immune Reconstitution Kinetics After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Children: A Maturation Block of IgM Memory B Cells May Lead to Impaired Antibody Immune Reconstitution. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl (2017) 23:1437–46. 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.05.005 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

