Closed-wedge Patelloplasty for the Treatment of Distal Patellofemoral Maltracking and Instability due to Severe Patellar Dysplasia: Case Report and Surgical Technique
- PMID: 34025801
- PMCID: PMC8121114
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10080-1501
Closed-wedge Patelloplasty for the Treatment of Distal Patellofemoral Maltracking and Instability due to Severe Patellar Dysplasia: Case Report and Surgical Technique
Abstract
Background: Patellofemoral maltracking is caused by different anatomical factors. Most of them are associated with a proximal maltracking, which alters the patella's engagement into the trochlear groove and predisposes the patellofemoral joint for instability. Different surgical techniques have been described to realign patellar tracking, however, most of which address proximal patellar maltracking.
Aim: The aim of this article is to demonstrate the influence of patella-related deformities on patellar tracking and to present a novel surgical technique for the treatment of distal patellar maltracking, caused by a severe patellar dyplasia.
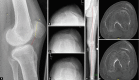
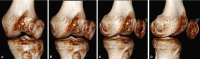
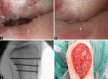
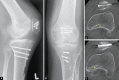
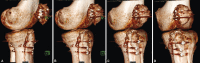
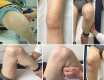
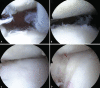
Case description: We report the case of a 23-year-old patient with a severe patellar dysplasia, presenting a distal patellar maltracking with recurring dislocations in deep flexion. Due to her instability, the patient was immobilised and dependent on the constant use of walking aids. Radiological images showed a concavely shaped patellar, which articulated exclusively with the lateral epicondyle and caused the patella to dislocate laterally, starting at a flexion angle of 60°. An anterior closing-wedge osteotomy was used to reshape and recenter the patella, which was complemented by a medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction. At the 18-month follow-up, the patient presented pain free and fully remobilised, without the use of walking aids. Patellar tracking was reestablished, with a possible knee flexion until 140°. No redislocation of the patella had occurred.
Conclusion: Distal patellofemoral maltracking, caused by a severe patellar dysplasia, can successfully be treated with an anterior closed-wedge osteotomy of the patella. In combination with a medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction, patellofemoral stability can be reestablished, to prevent further dislocations.
Clinical significance: There are multiple factors, which may cause patellar maltracking. A thorough clinical and radiological preoperative analysis is mandatory, in order to clearly identify the underlying pathologies, as these may affect patellar tracking proximally or distally.
How to cite this article: Frings J, Freudenthaler F, Krause M, et al. Closed-wedge Patelloplasty for the Treatment of Distal Patellofemoral Maltracking and Instability due to Severe Patellar Dysplasia: Case Report and Surgical Technique. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr 2020;15(3):184-192.
Keywords: Distal maltracking; Instability; Maltracking; Osteotomy; Patella; Patelloplasty.
Copyright © 2020; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Patellar dislocation : Causes and treatment].Unfallchirurg. 2020 Dec;123(12):969-983. doi: 10.1007/s00113-020-00912-5. Unfallchirurg. 2020. PMID: 33201266 German.
-
A High-Grade J Sign Is More Likely to Yield Higher Postoperative Patellar Laxity and Residual Maltracking in Patients With Recurrent Patellar Dislocation Treated With Derotational Distal Femoral Osteotomy.Am J Sports Med. 2020 Jan;48(1):117-127. doi: 10.1177/0363546519884669. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Am J Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 31765235
-
Combined distal femoral osteotomy (DFO) in genu valgum leads to reliable patellar stabilization and an improvement in knee function.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018 Dec;26(12):3572-3581. doi: 10.1007/s00167-018-5000-9. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018. PMID: 29869201
-
Inconsistencies in Reporting Risk Factors for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Failure: A Systematic Review.Am J Sports Med. 2022 Mar;50(3):867-877. doi: 10.1177/03635465211003342. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Am J Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 33914648
-
[Patella dislocation in athletes].Chirurg. 2014 Oct;85(10):879-87. doi: 10.1007/s00104-014-2772-4. Chirurg. 2014. PMID: 25182007 Review. German.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

