The association of endothelin-1 gene polymorphism and its plasma levels with hypertension and coronary atherosclerosis
- PMID: 34025830
- PMCID: PMC8130481
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2019.86770
The association of endothelin-1 gene polymorphism and its plasma levels with hypertension and coronary atherosclerosis
Abstract
Introduction: Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is the most potent among all vasoconstrictors, and its association with cardiovascular diseases has been reported before. Our aim was to investigate the association of ET-1 plasma level and its gene polymorphisms (rs5370 and rs10478694) with hypertension and coronary atherosclerosis (CA).
Material and methods: This study was carried out on 128 women and 132 men, who were divided into 4 groups: hypertensive without atherosclerosis (H+A-); hypertensive with atherosclerosis (H+A+); non-hypertensive with atherosclerosis (H-A+); and non-hypertensive without atherosclerosis (control group). Endothelin-1 plasma levels were measured by ELISA, and gene polymorphisms were detected by polymerase chain reaction - restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) methods. Coronary artery diseases (CAD) were then defined based on angiography data.
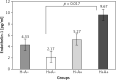
Results: The ET-1 plasma level was significantly higher in the H+A+ group in comparison with the other groups, especially H+A-. Comparing people with CA and those without it, the highest frequency level of the T allele of rs5370 was found in people with CA. Significantly higher frequencies of the 3A allele were detected in hypertensive patients in comparison with non-hypertensive individuals, when analyzing rs10478694.
Conclusions: Endothelin-1 plasma level shows a direct association with the risk of CA development. The T allele of rs5370 can be regarded as a risk factor for CA development. The 3A allele of rs10478694 can be associated with the risk of hypertension; therefore, it can be concluded that ET-1 and its gene polymorphisms play an important role in CA development and hypertension observed in the south-eastern populations of Iran.
Keywords: SNP; atherosclerosis; endothelin-1; hypertension; rs1046872; rs5370.
Copyright: © 2019 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Peto H, Corder R, Janes RW, Wallace BA. A molecular model for human Big-Endothelin-1 (Big ET-1) FEBS Lett. 1996;394:191–5. - PubMed
-
- Schiffrin EL. Vascular endothelin in hypertension. Vascul Pharmacol. 2005;43:19–29. - PubMed
-
- Forouzanfar MH, Liu P, Roth GA, et al. Global burden of hypertension and systolic blood pressure of at least 110 to 115 mm Hg, 1990-2015. JAMA. 2017;317:165–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
