The Effects of High Mineral Alkaline Water Consumed Over Three Consecutive Days on Reaction Time Following Anaerobic Exercise - A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Crossover Pilot Study
- PMID: 34025869
- PMCID: PMC8120973
- DOI: 10.2478/hukin-2021-0046
The Effects of High Mineral Alkaline Water Consumed Over Three Consecutive Days on Reaction Time Following Anaerobic Exercise - A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Crossover Pilot Study
Abstract
Drinking alkaline water after intense anaerobic exercise may enhance both cognitive and physical performance. This study aimed to investigate the effect of high mineral alkaline water consumed over three consecutive days on reaction time after anaerobic exercise in twelve healthy young males (aged 21.1 ± 1.3 years) with a valid sports medical examination. Participants were excluded when they took any medications or performance-enhancing supplements for the period of at least four weeks before the study commenced. Participants were randomly divided into two groups in this double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover pilot study. They ingested either alkaline water (AW) or regular table water ( RTW) for three consecutive days before anaerobic exercise. The anaerobic exercise consisted of two 2-min high-intensity step-tests with a passive rest interval of 3 minutes between the two bouts of exercise. Performance in the step-test (W), reaction time for visual and auditory signals, the rate of perceived exertion (RPE), urine specific gravity, and lactate concentration were analysed. No effect of AW was found on reaction time and the other variables except anaerobic performance. An-aerobic performance was significantly higher after ingestion of AW in both step-tests (p < 0.05). The ingestion of AW for three consecutive days before anaerobic exercise seems to positively affect anaerobic performance.
Keywords: Rate of Perceived Exertion; buffer system; exercise; step-test.
© 2021 Michal Steffl, Ivana Kinkorova, Karolina Talar, Tereza Jandova, Karolina Moulisova, Dan Omcirk, Jan Malecek, Jan Chrudimsky, Michał Wilk, Petr Stastny, Miroslav Petr, published by Sciendo.
Figures

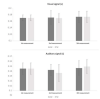
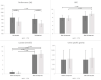
References
-
- Borg GA. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1982;14:377–381. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
