Tumor Exosomes Reprogrammed by Low pH Are Efficient Targeting Vehicles for Smart Drug Delivery and Personalized Therapy against their Homologous Tumor
- PMID: 34026432
- PMCID: PMC8132050
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202002787
Tumor Exosomes Reprogrammed by Low pH Are Efficient Targeting Vehicles for Smart Drug Delivery and Personalized Therapy against their Homologous Tumor
Abstract
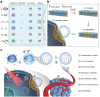
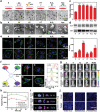
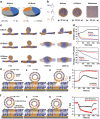
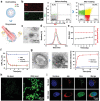
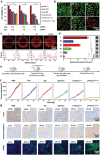
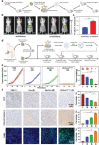
As membrane-bound extracellular vesicles, exosomes have targeting ability for specific cell types, and the cellular environment strongly impacts their content and uptake efficiency. Inspired by these natural properties, the impacts of various cellular stress conditions on the uptake efficiency of tumor iterated exosomes are evaluated, and low-pH treatment caused increased uptake efficiency and retained cell-type specificity is found. Lipidomics analyses and molecular dynamics simulations reveal a glycerolipid self-aggregation-based mechanism for the enhanced homologous uptake. Furthermore, these low-pH reprogrammed exosomes are developed into a smart drug delivery platform, which is capable of specifically targeting tumor cells and selectively releasing diverse chemodrugs in response to the exosome rupture by the near-infrared irradiance-triggered burst of reactive oxygen species. This platform exerts safe and enhanced antitumor effects demonstrated by multiple model mice experiments. These results open a new avenue to reprogram exosomes for smart drug delivery and potentially personalized therapy against their homologous tumor.
Keywords: combination therapy; lipids rearrangement; low pH reprogramming; patient‐derived xenografts; tumor exosomes.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Thery C., Zitvogel L., Amigorena S., Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569. - PubMed
-
- Tkach M., Thery C., Cell 2016, 164, 1226. - PubMed
-
- Simons M., Raposo G., Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 575. - PubMed
-
- Syn N. L., Wang L., Chow E. K., Lim C. T., Goh B. C., Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 665. - PubMed
-
- Farooqi A. A., Desai N. N., Qureshi M. Z., Librelotto D. R. N., Gasparri M. L., Bishayee A., Nabavi S. M., Curti V., Daglia M., Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
