A Dimension Reduction Approach for Energy Landscape: Identifying Intermediate States in Metabolism-EMT Network
- PMID: 34026435
- PMCID: PMC8132071
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202003133
A Dimension Reduction Approach for Energy Landscape: Identifying Intermediate States in Metabolism-EMT Network
Abstract
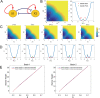
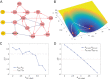
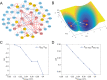
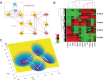
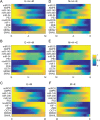
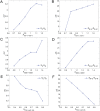
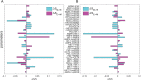
Dimension reduction is a challenging problem in complex dynamical systems. Here, a dimension reduction approach of landscape (DRL) for complex dynamical systems is proposed, by mapping a high-dimensional system on a low-dimensional energy landscape. The DRL approach is applied to three biological networks, which validates that new reduced dimensions preserve the major information of stability and transition of original high-dimensional systems. The consistency of barrier heights calculated from the low-dimensional landscape and transition actions calculated from the high-dimensional system further shows that the landscape after dimension reduction can quantify the global stability of the system. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and abnormal metabolism are two hallmarks of cancer. With the DRL approach, a quadrastable landscape for metabolism-EMT network is identified, including epithelial (E), abnormal metabolic (A), hybrid E/M (H), and mesenchymal (M) cell states. The quantified energy landscape and kinetic transition paths suggest that for the EMT process, the cells at E state need to first change their metabolism, then enter the M state. The work proposes a general framework for the dimension reduction of a stochastic dynamical system, and advances the mechanistic understanding of the underlying relationship between EMT and cellular metabolism.
Keywords: dimension reduction; energy landscape; epithelial‐mesenchymal transitions; gene regulatory networks; transition paths.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdi H., Williams L. J., Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433.
-
- Ye J., Janardan R., Li Q., in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA: 2005, pp. 1569–1576.
-
- Roweis S. T., Saul L. K., Science 2000, 290, 2323. - PubMed
-
- Maaten L. v. d., Hinton G., J. Mach. Learning Res. 2008, 9, 2579.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
