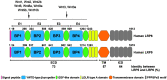
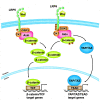
LRP5 and LRP6 in Wnt Signaling: Similarity and Divergence
- PMID: 34026761
- PMCID: PMC8134664
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.670960
LRP5 and LRP6 in Wnt Signaling: Similarity and Divergence
Abstract
The canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling plays a fundamental role in regulating embryonic development, injury repair and the pathogenesis of human diseases. In vertebrates, low density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 (LRP5 and LRP6), the single-pass transmembrane proteins, act as coreceptors of Wnt ligands and are indispensable for Wnt signal transduction. LRP5 and LRP6 are highly homologous and widely co-expressed in embryonic and adult tissues, and they share similar function in mediating Wnt signaling. However, they also exhibit distinct characteristics by interacting with different protein partners. As such, each of them possesses its own unique functions. In this review, we systematically discuss the similarity and divergence of LRP5 and LRP6 in mediating Wnt and other signaling in the context of kidney diseases. A better understanding of the precise role of LRP5 and LRP6 may afford us to identify and refine therapeutic targets for the treatment of a variety of human diseases.
Keywords: LRP5; LRP6; Wnt; YAP; chronic kidney disease; kidney fibrosis; β-catenin.
Copyright © 2021 Ren, Chen and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

