Metabolism and Chronic Inflammation: The Links Between Chronic Heart Failure and Comorbidities
- PMID: 34026868
- PMCID: PMC8131678
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.650278
Metabolism and Chronic Inflammation: The Links Between Chronic Heart Failure and Comorbidities
Abstract
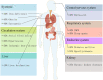
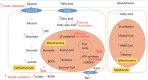
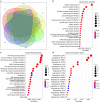
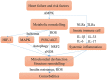
Heart failure (HF) patients often suffer from multiple comorbidities, such as diabetes, atrial fibrillation, depression, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and chronic kidney disease. The coexistance of comorbidities usually leads to multi morbidity and poor prognosis. Treatments for HF patients with multi morbidity are still an unmet clinical need, and finding an effective therapy strategy is of great value. HF can lead to comorbidity, and in return, comorbidity may promote the progression of HF, creating a vicious cycle. This reciprocal correlation indicates there may be some common causes and biological mechanisms. Metabolism remodeling and chronic inflammation play a vital role in the pathophysiological processes of HF and comorbidities, indicating metabolism and inflammation may be the links between HF and comorbidities. In this review, we comprehensively discuss the major underlying mechanisms and therapeutic implications for comorbidities of HF. We first summarize the potential role of metabolism and inflammation in HF. Then, we give an overview of the linkage between common comorbidities and HF, from the perspective of epidemiological evidence to the underlying metabolism and inflammation mechanisms. Moreover, with the help of bioinformatics, we summarize the shared risk factors, signal pathways, and therapeutic targets between HF and comorbidities. Metabolic syndrome, aging, deleterious lifestyles (sedentary behavior, poor dietary patterns, smoking, etc.), and other risk factors common to HF and comorbidities are all associated with common mechanisms. Impaired mitochondrial biogenesis, autophagy, insulin resistance, and oxidative stress, are among the major mechanisms of both HF and comorbidities. Gene enrichment analysis showed the PI3K/AKT pathway may probably play a central role in multi morbidity. Additionally, drug targets common to HF and several common comorbidities were found by network analysis. Such analysis has already been instrumental in drug repurposing to treat HF and comorbidity. And the result suggests sodium-glucose transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors, IL-1β inhibitors, and metformin may be promising drugs for repurposing to treat multi morbidity. We propose that targeting the metabolic and inflammatory pathways that are common to HF and comorbidities may provide a promising therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: chronic inflammation; comorbidities; heart failure; metabolism; mitochondria; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Zhao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic aging fuels heart failure: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic avenues.ESC Heart Fail. 2025 Apr;12(2):1059-1080. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14947. Epub 2024 Jul 22. ESC Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 39034866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
The role of sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors in heart failure and chronic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes.Curr Med Res Opin. 2019 Jul;35(7):1283-1295. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2019.1576479. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019. PMID: 30767677 Review.
-
Myocardial metabolism in heart failure: Purinergic signalling and other metabolic concepts.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Feb;194:132-144. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.08.015. Epub 2018 Aug 25. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30149104 Review.
-
Reappraising the role of chronic inflammatory burden in heart failure.J Gene Med. 2023 Aug;25(8):e3519. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3519. Epub 2023 May 21. J Gene Med. 2023. PMID: 37211702
Cited by
-
The Influence of Abdominal Adiposity and Physical Fitness on Obesity Status of Portuguese Adolescents.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 7;19(18):11213. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191811213. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36141486 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence estimates of the insulin resistance and associated prevalence of heart failure among United Status adults.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Jun 10;23(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03294-9. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37301866 Free PMC article.
-
The Usefulness of C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio in the Prediction of Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Coronary Chronic Total Occlusion Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 12;8:731261. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.731261. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34869630 Free PMC article.
-
Serum potassium in elderly heart failure patients as a predictor of readmission within 1 year.Heart Vessels. 2023 Apr;38(4):507-516. doi: 10.1007/s00380-022-02192-y. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Heart Vessels. 2023. PMID: 36318301
-
Enhancing Comprehensive Assessments in Chronic Heart Failure Caused by Ischemic Heart Disease: The Diagnostic Utility of Holter ECG Parameters.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Aug 14;60(8):1315. doi: 10.3390/medicina60081315. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39202596 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

