Role of N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 34026872
- PMCID: PMC8138049
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.659628
Role of N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
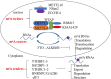
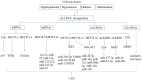
Despite treatments being improved and many risk factors being identified, cardiovascular disease (CVD) is still a leading cause of mortality and disability worldwide. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most common, abundant, and conserved internal modification in RNAs and plays an important role in the development of CVD. Many studies have shown that aabnormal m6A modifications of coding RNAs are involved in the development of CVD. In addition, non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) exert post-transcriptional regulation in many diseases including CVD. Although ncRNAs have also been found to be modified by m6A, the studies on m6A modifications of ncRNAs in CVD are currently lacking. In this review, we summarized the recent progress in understanding m6A modifications in the context of coding RNAs and ncRNAs, as well as their regulatory roles in CVD.
Keywords: CVD; M6A; mRNAs; modification; non-coding RNAs.
Copyright © 2021 Song, Hou, Wu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The landscape of epigenetic regulation and therapeutic application of N6-methyladenosine modifications in non-coding RNAs.Genes Dis. 2023 Jul 18;11(5):101045. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.06.015. eCollection 2024 Sep. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 38988321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Mutual Regulation of m6A Modification and Non-Coding RNAs in Atherosclerosis.Int J Gen Med. 2025 Feb 25;18:1047-1073. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S508197. eCollection 2025. Int J Gen Med. 2025. PMID: 40026815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of N6-methyladenosine-modified non-coding RNAs in the pathological process of human cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Jul 18;8(1):325. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01113-2. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35851061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNA-Mediated N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) deposition: A pivotal regulator of cancer, impacting key signaling pathways in carcinogenesis and therapy response.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Nov 13;9(1):84-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.11.005. eCollection 2024 Mar. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 38075202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New understandings of the genetic regulatory relationship between non-coding RNAs and m6A modification.Front Genet. 2023 Dec 6;14:1270983. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1270983. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 38125749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The critical role of epigenetic mechanism in PM2.5-induced cardiovascular diseases.Genes Environ. 2021 Oct 15;43(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s41021-021-00219-w. Genes Environ. 2021. PMID: 34654488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL3 regulates autophagy of hypoxia-induced cardiomyocytes by targeting ATG7.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Feb 1;11(1):37. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02320-3. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 39893158 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased METTL3 in atrial myocytes promotes atrial fibrillation.Europace. 2025 Feb 5;27(2):euaf021. doi: 10.1093/europace/euaf021. Europace. 2025. PMID: 39991872 Free PMC article.
-
METTL14-mediated m6A methylation of pri-miR-5099 to facilitate cardiomyocyte pyroptosis in myocardial infarction.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Jun;46(6):1639-1651. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01485-y. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39939804
-
Role of m6A Methylation in the Occurrence and Development of Heart Failure.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 24;9:892113. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.892113. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35811741 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

