Non-cancer clinical trials start-up metrics at an academic medical center: Implications for advancing research
- PMID: 34027224
- PMCID: PMC8121646
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conctc.2021.100774
Non-cancer clinical trials start-up metrics at an academic medical center: Implications for advancing research
Abstract
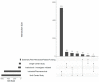
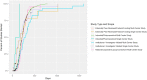
The primary goal for any clinical trial after it receives a funding notification is to receive regulatory approval and initiate the trial for recruitment. Every trial must go through documentation and regulatory process before it can start recruiting participants and collecting data; this initial process of review and approval is known as the study start-up process (SSU). We evaluated the average time taken for studies to receive approvals. Using data from clinical trials conducted at the University of Kansas Medical Center, various times to reach the start of the study were calculated based on the dates of individual study. The results of this analysis showed that chart review studies and investigator-initiated trials had a shorter time to activation than other types of studies. Additionally, single-center studies had a shorter activation time than multi-center studies. The analysis also demonstrated that the overall processing time consistently had been reduced over time.
Keywords: Clinical trial activation; Institutional review board review.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Dilts D.M., Sandler A., Cheng S., Crites J., Ferranti L., Wu A., Gray R., MacDonald J., Marinucci D., Comis R. Development of clinical trials in a cooperative group setting: the eastern cooperative oncology group. Clin. Canc. Res. 2008;14:3427–3433. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-5060. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dilts D.M., Sandler A.B., Baker M., Cheng S.K., George S.L., Karas K.S., McGuire S., Menon G.S., Reusch J., Sawyer D., Scoggins M., Wu A., Zhou K., Schilsky R.L. Processes to activate phase III clinical trials in a cooperative oncology group: the case of cancer and leukemia group B. J. Clin. Orthod. 2006;24:4553–4557. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.06.7819. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lamberti Mary Jo. Clinical trials take a long time to get started. Here's how to speed it up. 2017. https://www.statnews.com/2018/03/28/clinical-trials-startup-speed/ [WWW Document]. STAT. URL. accessed 3.19.20.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources