Capturing dynamic biological signals via bio-mimicking hydrogel for precise remodeling of soft tissue
- PMID: 34027237
- PMCID: PMC8134719
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.04.039
Capturing dynamic biological signals via bio-mimicking hydrogel for precise remodeling of soft tissue
Abstract
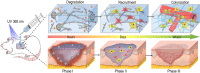
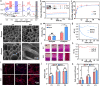
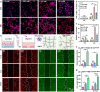
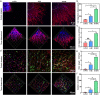
Soft tissue remodeling is a sophisticated process that sequentially provides dynamic biological signals to guide cell behavior. However, capturing these signals within hydrogel and directing over time has still been unrealized owing to the poor comprehension of physiological processes. Here, a bio-mimicking hydrogel is designed via thiol-ene click reaction to capture the early physical signal triggered by inflammation, and the chemical signals provided with chemokine and natural adhesion sites, which guaranteed the precise soft tissue remodeling. This bio-mimicking hydrogel efficiently facilitated cell anchoring, migration, and invasion in the 3D matrix due to the permissive space and the interaction with integrin receptors. Besides, the covalently grafted chemokine-like peptide is optimal for colonization and functional differentiation of endothelial cells through a HIF-1α dependent signal pathway. Furthermore, the early polarization of macrophages, collagen deposition and angiogenesis in rat acute wound model, and the increased blood perfusion in mouse skin flap model have confirmed that the bio-mimicking hydrogel realized precise soft tissue remodeling and opens new avenues for the phased repair of different tissues such as nerve, myocardium, and even bone.
Keywords: Biological signals; Chemotactic; Hydrogel; Physiological phase; Soft tissue remodeling.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cell-instructive pectin hydrogels crosslinked via thiol-norbornene photo-click chemistry for skin tissue engineering.Acta Biomater. 2018 Jan 15;66:282-293. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.11.016. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29128530
-
Prostaglandin E2 hydrogel improves cutaneous wound healing via M2 macrophages polarization.Theranostics. 2018 Oct 22;8(19):5348-5361. doi: 10.7150/thno.27385. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 30555551 Free PMC article.
-
Modifying decellularized aortic valve scaffolds with stromal cell-derived factor-1α loaded proteolytically degradable hydrogel for recellularization and remodeling.Acta Biomater. 2019 Apr 1;88:280-292. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.02.002. Epub 2019 Feb 2. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30721783
-
A chondrogenesis induction system based on a functionalized hyaluronic acid hydrogel sequentially promoting hMSC proliferation, condensation, differentiation, and matrix deposition.Acta Biomater. 2021 Mar 1;122:145-159. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.054. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33444801
-
Tunable Adhesion for Bio-Integrated Devices.Micromachines (Basel). 2018 Oct 18;9(10):529. doi: 10.3390/mi9100529. Micromachines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30424462 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Functional Hydrogel for Repair of Abdominal Wall Defects: A Review.Biomater Res. 2024 Jun 6;28:0031. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0031. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 38845842 Free PMC article.
-
3D Printing-Based Hydrogel Dressings for Wound Healing.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec;11(47):e2404580. doi: 10.1002/advs.202404580. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39552255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in extracellular vesicle functionalization strategies for tissue regeneration.Bioact Mater. 2022 Aug 11;25:500-526. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.07.022. eCollection 2023 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 37056271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenesis in Atrial Fibrillation: A Literature Review.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 6;13(6):1399. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061399. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrospun fiber-based immune engineering in regenerative medicine.Smart Med. 2024 Feb 24;3(1):e20230034. doi: 10.1002/SMMD.20230034. eCollection 2024 Feb. Smart Med. 2024. PMID: 39188511 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li X., Cho B., Martin R., Seu M., Zhang C., Zhou Z., Choi J.S., Jiang X., Chen L., Walia G., Yan J., Callanan M., Liu H., Colbert K., Morrissette-McAlmon J., Grayson W., Reddy S., Sacks J.M., Mao H.Q. Nanofiber-hydrogel composite–mediated angiogenesis for soft tissue reconstruction. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019;11(490) - PubMed
-
- Raghow R. The role of extracellular matrix in postinflammatory wound healing and fibrosis. Faseb. J. 1994;8(11):823–831. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

