Correlation of the Single-Assessment Numeric Evaluation (SANE) Score With Hip-Specific Patient-Reported Outcome Measures
- PMID: 34027452
- PMCID: PMC8129469
- DOI: 10.1016/j.asmr.2020.10.008
Correlation of the Single-Assessment Numeric Evaluation (SANE) Score With Hip-Specific Patient-Reported Outcome Measures
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine if the Single-Assessment Numeric Evaluation (SANE) score correlates with existing validated hip-specific patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs), including the Modified Harris Hip Score (mHHS), the International Hip Outcome Tool (IHOT-33), the Hip Outcome Score, Activities of Daily Living subscale (HOS-ADL), and the Hip Outcome Score, Sport-Specific subscale (HOS-SS), for patients preparing to undergo hip arthroscopy for treatment of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAIS).
Methods: A single surgeon's operative database was retrospectively reviewed to identify patients undergoing primary hip arthroscopy for treatment of FAIS from April 2018 to October 2019. Patient-specific factors including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), and duration of symptoms were collected. Preoperative SANE, mHHS, IHOT-33, HOS-ADL, and HOS-SS scores were analyzed. Statistical analysis using Pearson correlation was performed to identify the relationship between the SANE score and the mHHS, IHOT-33, HOS-ADL, and HOS-SS, preoperatively.
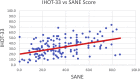
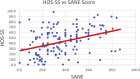
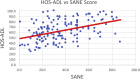
Results: 154 patients were included in the study. The mean mHHS was 54.4 ± 11.7; mean IHOT-33 score was 32.7 ± 15.0; mean HOS-SS 42.9 ± 23.7; and mean HOS-ADL was 63.3 ± 1. The mean SANE score was 36.7 ± 19.9. The Simple Hip Score was directly correlated with the mHHS (P < .01), the IHOT-33 (P < .01); the HOS-ADL (P < .01), and the HOS-SS (P < .01). The mean patient age was 35.9 years; 109 (70.8%) were female and 45 (29.2%) were male. Average patient BMI was 26.9. At the time of patient completion of the questionnaire, the majority of patients (65%) had been having symptoms for >1 year.
Conclusion: The SANE score was strongly correlated with mHHS, IHOT-33, HOS-ADL, and HOS-SS in the preoperative setting for patients undergoing hip arthroscopy for treatment of FAIS. Given its simplicity, SANE may be a valuable tool for rapid assessment of joint function and pain in this patient population.
Level of evidence: IV, therapeutic case series.
© 2020 by the Arthroscopy Association of North America. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Bozic K.J., Chan V., Valone F.H., 3rd, Feeley B.T., Vail T.P. Trends in hip arthroscopy utilization in the United States. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28:140–143. - PubMed
-
- Kelly B.T., Williams R.J., 3rd, Philippon M.J. Hip arthroscopy: Current indications, treatment options, and management issues. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31:1020–1037. - PubMed
-
- Gagnier J.J. Patient reported outcomes in orthopaedics. J Orthop Res. 2017;35:2098–2108. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

