LIM domain proteins in cell mechanobiology
- PMID: 34028199
- PMCID: PMC8603407
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.21677
LIM domain proteins in cell mechanobiology
Abstract
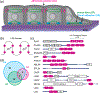
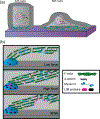
The actin cytoskeleton is important for maintaining mechanical homeostasis in adherent cells, largely through its regulation of adhesion and cortical tension. The LIM (Lin-11, Isl1, MEC-3) domain-containing proteins are involved in a myriad of cellular mechanosensitive pathways. Recent work has discovered that LIM domains bind to mechanically stressed actin filaments, suggesting a novel and widely conserved mechanism of mechanosensing. This review summarizes the current state of knowledge of LIM protein mechanosensitivity.
Keywords: LIM proteins; actin cytoskeleton; adherens junctions; focal adhesions.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
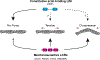

References
-
- Brown MC, Perrotta JA, & Turner CE (1996). Identification of LIM3 as the principal determinant of paxillin focal adhesion localization and characterization of a novel motif on paxillin directing vinculin and focal adhesion kinase binding. The Journal of Cell Biology, 135(4), 1109–1123. 10.1083/jcb.135.4.1109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

