The journey of antimalarial drugs against SARS-CoV-2: Review article
- PMID: 34028468
- PMCID: PMC8132553
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imu.2021.100604
The journey of antimalarial drugs against SARS-CoV-2: Review article
Abstract
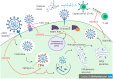
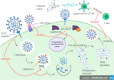
The recent outbreak of coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19) introduced by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has greatly affected the global public health. This pandemic disease became particularly threatening after the start of a new wave. Vaccines of tested efficacy to stop COVID-19 infection are being investigated vigorously worldwide. Currently, some specific drugs have been authorized for COVID-19, but the improvement of antivirals requires time. Hence, a faster way of treatment is done by drug repurposing. Repurposing of drugs is promising for treating and reducing the symptoms of the disease, and it a fast, easy, and safe method to address the crisis, because of their previously known applications. Some antimalarial drugs, especially chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine, have been repurposed, as they exhibited promising results in vitro and in vivo. This article investigates repurposed antimalarial drugs, focusing on their antiviral mechanisms of action, effects in combinations, trial results, and their side effects.
Keywords: Anti-malarial drugs; COIVD-19; Combination therapy; Drug repurposing.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repurposed Drugs during the Outbreak of Pandemic COVID-19: A Mini-Review on Their Molecular Structures and Hit-and-Trial Results.ACS Omega. 2024 Aug 20;9(35):36858-36864. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05357. eCollection 2024 Sep 3. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39246499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into antiviral mechanisms of remdesivir, lopinavir/ritonavir and chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine affecting the new SARS-CoV-2.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110668. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110668. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32861965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of COVID-19.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Apr;24(8):4539-4547. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202004_21038. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32373993 Review.
-
Drugs repurposing for SARS-CoV-2: new insight of COVID-19 druggability.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022 Sep;20(9):1187-1204. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2022.2082944. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022. PMID: 35615888
-
Impact of repurposed drugs on the symptomatic COVID-19 patients.J Infect Public Health. 2021 Jan;14(1):24-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.11.009. Epub 2020 Dec 7. J Infect Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33341481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Just a Reflection: Does Drug Repurposing Perpetuate Sex-Gender Bias in the Safety Profile?Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Jul 27;14(8):730. doi: 10.3390/ph14080730. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review of the Global Intervention for SARS-CoV-2 Combating: From Drugs Repurposing to Molnupiravir Approval.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Mar 15;16:685-715. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S354841. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 35321497 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the structure-activity relationship of marine natural polyketides as promising SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors.RSC Adv. 2021 Sep 22;11(50):31339-31363. doi: 10.1039/d1ra05817g. eCollection 2021 Sep 21. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35496831 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Potential Anti-SARS-CoV-2 and Anti-MERS-CoV Activities of Yellow Necklacepod among Three Selected Medicinal Plants: Extraction, Isolation, Identification, In Vitro, Modes of Action, and Molecular Docking Studies.Metabolites. 2022 Nov 13;12(11):1109. doi: 10.3390/metabo12111109. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36422249 Free PMC article.
-
Squaramide Tethered Clindamycin, Chloroquine, and Mortiamide Hybrids: Design, Synthesis, and Antimalarial Activity.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023 Jan 25;14(2):217-222. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00531. eCollection 2023 Feb 9. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 36793432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakowski M.A., et al. Oral drug repositioning candidates and synergistic remdesivir combinations for the prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19. BioRxiv. 2020
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous