Construction of TME and Identification of crosstalk between malignant cells and macrophages by SPP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 34028567
- PMCID: PMC10992184
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-021-02967-8
Construction of TME and Identification of crosstalk between malignant cells and macrophages by SPP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
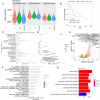
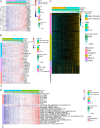
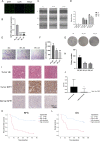
Liver cancer accounts for 6% of all malignancies causing death worldwide, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common histological type. HCC is a heterogeneous cancer, but how the tumour microenvironment (TME) of HCC contributes to the progression of HCC remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the immune microenvironment by multiomics analysis. The tumour immune infiltration characteristics of HCC were determined at the genomic, epigenetic, bulk transcriptome and single-cell levels by data from The Cancer Genome Atlas portal and the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). An epigenetic immune-related scoring system (EIRS) was developed to stratify patients with poor prognosis. SPP1, one gene in the EIRS system, was identified as an immune-related predictor of poor survival in HCC patients. Through receptor-ligand pair analysis in single-cell RNA-seq, SPP1 was indicated to mediate the crosstalk between HCC cells and macrophages via SPP1-CD44 and SPP1-PTGER4 association. In vitro experiments further validate SPP1 can trigger the polarization of macrophages to M2-phenotype tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs).
Keywords: Crosstalk; Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); Prognosis; SPP1; Tumour microenvironment (TME); Tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs).
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lu L, Jiang J, Zhan M, Zhang H, Wang QT, Sun SN, et al. (2020) Targeting neoantigens in hepatocellular carcinoma for immunotherapy: A futile strategy? Hepatology 73(1):414–421 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

