Pharmacological treatment of hypertension in people without prior cerebrovascular disease for the prevention of cognitive impairment and dementia
- PMID: 34028812
- PMCID: PMC8142793
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004034.pub4
Pharmacological treatment of hypertension in people without prior cerebrovascular disease for the prevention of cognitive impairment and dementia
Abstract
Background: This is an update of a Cochrane Review first published in 2006 (McGuinness 2006), and previously updated in 2009 (McGuinness 2009). Hypertension is a risk factor for dementia. Observational studies suggest antihypertensive treatment is associated with lower incidences of cognitive impairment and dementia. There is already clear evidence to support the treatment of hypertension after stroke.
Objectives: To assess whether pharmacological treatment of hypertension can prevent cognitive impairment or dementia in people who have no history of cerebrovascular disease.
Search methods: We searched the Specialised Register of the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, three other databases, as well as many trials registries and grey literature sources, most recently on 7 July 2020.
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) in which pharmacological interventions to treat hypertension were given for at least 12 months. We excluded trials of pharmacological interventions to lower blood pressure in non-hypertensive participants. We also excluded trials conducted solely in people with stroke.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted data. We contacted study authors for additional information. We collected information regarding incidence of dementia, cognitive decline, change in blood pressure, adverse effects and quality of life. We assessed the certainty of evidence using GRADE.
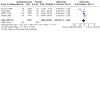
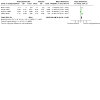
Main results: We included 12 studies, totaling 30,412 participants, in this review. Eight studies compared active treatment with placebo. Of the four non-placebo-controlled studies, two compared intensive versus standard blood pressure reduction. The two final included studies compared different classes of antihypertensive drug. Study durations varied from one to five years. The combined result of four placebo-controlled trials that reported incident dementia indicated no evidence of a difference in the risk of dementia between the antihypertensive treatment group and the placebo group (236/7767 versus 259/7660, odds ratio (OR) 0.89, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.72 to 1.09; very low certainty evidence, downgraded due to study limitations and indirectness). The combined results from five placebo-controlled trials that reported change in Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) may indicate a modest benefit from antihypertensive treatment (mean difference (MD) 0.20, 95% CI 0.10 to 0.29; very low certainty evidence, downgraded due to study limitations, indirectness and imprecision). The certainty of evidence for both cognitive outcomes was downgraded on the basis of study limitations and indirectness. Study durations were too short, overall, to expect a significant difference in dementia rates between groups. Dementia and cognitive decline were secondary outcomes for most studies. Additional sources of bias include: the use of antihypertensive medication by the placebo group in the placebo-controlled trials; failure to reach recruitment targets; and early termination of studies on safety grounds. Meta-analysis of the placebo-controlled trials reporting results found a mean change in systolic blood pressure of -9.25 mmHg (95% CI -9.73, -8.78) between treatment (n = 8973) and placebo (n = 8820) groups, and a mean change in diastolic blood pressure of -2.47 mmHg (95% CI -2.70, -2.24) between treatment (n = 7700) and placebo (n = 7509) groups (both low certainty evidence downgraded on the basis of study limitations and inconsistency). Three trials - SHEP 1991, LOMIR MCT IL 1996 and MRC 1996 - reported more withdrawals due to adverse events in active treatment groups than placebo groups. Participants on active treatment in Syst Eur 1998 were less likely to discontinue treatment due to side effects, and participants on active treatment in HYVET 2008 reported fewer 'serious adverse events' than in the placebo group. There was no evidence of a difference in withdrawals rates between groups in SCOPE 2003, and results were unclear for Perez Stable 2000 and Zhang 2018. Heterogeneity precluded meta-analysis. Five of the placebo-controlled trials provided quality of life (QOL) data. Heterogeneity again precluded meta-analysis. SHEP 1991, Syst Eur 1998 and HYVET 2008 reported no evidence of a difference in QOL measures between active treatment and placebo groups over time. The SCOPE 2003 sub-study (Degl'Innocenti 2004) showed a smaller drop in QOL measures in the active treatment compared to the placebo group. LOMIR MCT IL 1996 reported an improvement in a QOL measure at twelve months in one active treatment group and deterioration in another.
Authors' conclusions: High certainty randomised controlled trial evidence regarding the effect of hypertension treatment on dementia and cognitive decline does not yet exist. The studies included in this review provide low certainty evidence (downgraded primarily due to study limitations and indirectness) that pharmacological treatment of hypertension, in people without prior cerebrovascular disease, leads to less cognitive decline compared to controls. This difference is below the level considered clinically significant. The studies included in this review also provide very low certainty evidence that pharmacological treatment of hypertension, in people without prior cerebrovascular disease, prevents dementia.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00122811.
Copyright © 2021 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures


Update of
-
Blood pressure lowering in patients without prior cerebrovascular disease for prevention of cognitive impairment and dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Oct 7;2009(4):CD004034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004034.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 24;5:CD004034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004034.pub4. PMID: 19821318 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
ACCORD MIND 2014 {published data only}
-
- Buse JB, Bigger JT, Byington RP, Cooper LS, Cushman WC, Friedewald WT, et al, ACCORD Study Group. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial: design and methods. American Journal of Cardiology 2007;99(12A):21i-33i. - PubMed
-
- Cushman WC, Grimm RH Jr, Cutler JA, Evans GW, Capes S, Corson MA, et al, ACCORD Study Group. Rationale and design for the blood pressure intervention of the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial. American Journal of Cardiology 2007;99(12A):44i-55i. - PubMed
-
- Launer LJ, Miller ME, Williamson JD, Lazar RM, Gerstein HC, Murray AM, et al, ACCORD MIND investigators. Effects of intensive glucose lowering on brain structure and function in people with type 2 diabetes (ACCORD MIND): a randomised open-label substudy. Lancet Neurology 2011;10(11):969-77. - PMC - PubMed
AVEC 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hajjar I, Hart M, Milberg W, Novak V, Lipsitz L. The rationale and design of the antihypertensives and vascular, endothelial, and cognitive function (AVEC) trial in elderly hypertensives with early cognitive impairment: role of the renin angiotensin system inhibition. BMC Geriatrics 2009;9:48. - PMC - PubMed
CAMUI 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sato N, Saijo Y, Hasebe N, CAMUI investigators. Combination of antihypertensive therapy in the elderly, multicenter investigation (CAMUI) trial. International Heart Journal 2012;53(4):244-8. - PubMed
-
- Sato N, Saijo Y, Sasagawa Y, Morimoto H, Takeuchi T, Sano H, Koyama S, Takehara N, Morita K, Sumitomo K, Maruyama J, Kikuchi K, Hasebe N, CAMUI investigators. Combination of antihypertensive therapy in the elderly, multicenter investigation (CAMUI) trial: results after 1 year. Journal of Hypertension 2013;31(6):1245-55. - PubMed
HYVET 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Beckett NS, Peters R, Fletcher AE, Staessen JA, Liu L, Dumiterscu D, et al, for the HYVET Study Group. Treatment of hypertension in patients 80 years of age or older. NEJM 2008;358:1887-1898. - PubMed
-
- Bulpitt C, Fletcher A, Beckett N, Coope J, Gil-Extremera B, Forette F, et al. Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial (HYVET): protocol for the main trial. Drugs & Aging 2001;18:151-164. - PubMed
-
- Peters R, Beckett N, Forette F, Tuomilehto J, Clarke R, Ritchie C, et al, for the HYVET investigators. Incident dementia and blood pressure lowering in the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial cognitive function assessment (HYVET-COG): a double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Lancet Neurology 2008;7:683-689. - PubMed
-
- Peters R, Beckett N, Nunes M, Fletcher A, Forette F, Bulpitt C. A substudy protocol of the Hypertension in the Very Elderly Trial assessing cognitive decline and dementia incidence (HYVET-COG): an ongoing randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Drugs Aging 2006;23:83-92. - PubMed
LOMIR MCT IL 1996 {published data only}
-
- Yodfat Y, Bar-On D, Amir M, Cristal N. Quality of life in normotensives compared to hypertensive men treated with isradipine or methyldopa as monotherapy or in combination with captopril: the LOMIR-MCT-IL study.. Journal of Human Hypertension 1996 Feb;10(2):117-22. - PubMed
-
- Yodfat Y, Cristal N. A multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of isradipine and methyldopa as monotherapy or in combination with captopril in the treatment of hypertension. The LOMIR-MCT-IH Research Group.. American Journal of Hypertension 1993 Mar;6(3 Pt 2):57S-61S. - PubMed
MRC 1996 {published data only}
Perez Stable 2000 {published data only}
-
- Pérez-Stable EJ, Halliday R, Gardiner PS, Baron RB, Hauck WW, Acree M, Coates TJ. The effects of propranolol on cognitive function and quality of life: a randomized trial among patients with diastolic hypertension.. The American Journal Of Medicine 2000 Apr 1;108(5):359-65. - PubMed
SCOPE 2003 {published data only}
-
- Degl'Innocenti A, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Lithell H, Olofsson B, Skoog I, Trenkwalder P, Zanchetti A, Wiklund I. Health-related quality of life during treatment of elderly patients with hypertension: results from the Study on COgnition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE). Journal of Human Hypertension 2004;18(4):239-45. - PubMed
-
- Lithell H, Hansson L, Skoog I, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Olofsson B, Trenkwalder P, Zanchetti A for the SCOPE Study Group. The Study of COgnition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE); outcomes in patients not receiving add-on therapy after randomization. Journal of Hypertension 2004;22(8):1605-12. - PubMed
-
- Lithell H, Hansson L, Skoog I, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Olofsson B, Trenkwalder P, Zanchetti A for the SCOPE Study Group. The Study on Cognition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE): principal results of a randomised double-blind intervention trial. Journal of Hypertension 2003;21:875-886. - PubMed
-
- Papademetriou V, Farsang C, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Lithell H, Olofsson B, Skoog I, Trenkwalder P, Zanchetti A for the SCOPE Study Group. Stroke Prevention With the Angiotension II Type-1 Receptor Blocker Candesartan in Elderly Patients With Isolated Systolic Hypertension. The Study on Cognition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE). Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2004;44(6):1175-80. - PubMed
-
- Skoog I, Lithell H, Hansson L, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Olofsson B, et al, for the SCOPE Study Group. Effect of baseline cognitive function and antihypertensive treatment on cognitive and cardiovascular outcomes: Study on COgnition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE). American Journal of Hypertension 2005;18:1052-1059. - PubMed
SHEP 1991 {published data only}
-
- Applegate WB, Pressel S, Wittes J, Luhr J, Shekelle RB, Camel GH, et al. Impact of the Treatment of Isolated Systolic Hypertension on Behavioral Variables. Results From the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program. Arch Intern Med 1994;154:2154-2160. - PubMed
-
- Di Bari M, Pahor M, Franse LV, Shorr RI, Wan JY, Ferrucci L, et al. Dementia and Disability Outcomes in Large Hypertension Trials: Lessons Learned from the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP) Trial. American Journal of Epidemiology 2001;153:72-8. - PubMed
-
- SHEP Cooperative Research Group. Prevention of Stroke by Antihypertensive Drug Treatment in Older Persons With Isolated Systolic Hypertension. Final Results of the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP). JAMA 1991;265:3255-64. - PubMed
-
- The Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP) Cooperative Research Group. Rationale and Design of a Randomized Clinical Trial on Prevention of Stroke in Isolated Systolic Hypertension. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1988;41:1197-1208. - PubMed
SPRINT MIND 2019 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ambrosius WT, Sink KM, Foy CG, Berlowitz DR, Cheung AK, Cushman WC, Fine LJ, Goff DC Jr, Johnson KC, Killeen AA, Lewis CE, Oparil S, Reboussin DM, Rocco MV, Snyder JK, Williamson JD, Wright JT Jr, Whelton PK, SPRINT Study Research Group. The design and rationale of a multicenter clinical trial comparing two strategies for control of systolic blood pressure: the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT).. Clinical Trials 2014 Oct;11(5):532-46. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berlowitz DR, Foy CG, Kazis LE, Bolin LP, Conroy MB, Fitzpatrick P, Gure TR, Kimmel PL, Kirchner K, Morisky DE, Newman J, Olney C, Oparil S, Pajewski NM, Powell J, Ramsey T, Simmons DL, Snyder J, Supiano MA, Weiner DE, Whittle J, SPRINT Research Group. Effect of Intensive Blood-Pressure Treatment on Patient-Reported Outcomes.. The New England Journal of Medicine 2017 Aug 24;377(8):733-744. - PMC - PubMed
-
- SPRINT Research Group, Wright JT Jr, Williamson JD, Whelton PK, Snyder JK, Sink KM, Rocco MV, Reboussin DM, Rahman M, Oparil S, Lewis CE, Kimmel PL, Johnson KC, Goff DC Jr, Fine LJ, Cutler JA, Cushman WC, Cheung AK, Ambrosius WT. A Randomized Trial of Intensive versus Standard Blood-Pressure Control.. The New England Journal of Medicine 2015 Nov 26;373(22):2103-16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williamson JD, Supiano MA, Applegate WB, Berlowitz DR, Campbell RC, Chertow GM, Fine LJ, Haley WE, Hawfield AT, Ix JH, Kitzman DW, Kostis JB, Krousel-Wood MA, Launer LJ, Oparil S, Rodriguez CJ, Roumie CL, Shorr RI, Sink KM, Wadley VG, Whelton PK, Whittle J, Woolard NF, Wright JT Jr, Pajewski NM, SPRINT Research Group. Intensive vs Standard Blood Pressure Control and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes in Adults Aged ≥75 Years: A Randomized Clinical Trial.. JAMA 2016 Jun 28;315(24):2673-82. - PMC - PubMed
Syst Eur 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Amery A, Birkenhager W, Bulpitt CJ, Clement D, De Leeuw P, Dollery CT, et al. Syst-Eur. A multicentre trial on the treatment of isolated systolic hypertension in the elderly: Objectives, protocol, and organization. Aging Clin Exp Res 1991;3:287-302. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher AE, Bulpitt CJ, Thijs L, Toumilehto J, Antikainen R, Bossini A, et al. Quality of life on randomised treatment for isolated hypertension: results from the Syst-Eur Trial. Journal of Hypertension 2002;20:2069-2079. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher AE, Bulpitt CJ, Tuomilehto J, Browne J, Bossini A, Kawecka-Jaszcz K, et al. Quality of life of elderly patients with isolated systolic hypertension: baseline data from the Syst-Eur Trial. Journal of Hypertension 1988;16:1117-1124. - PubMed
-
- Forette F, Seux M-L, Staessen JA, Thijs L, Babarskiene M-R, Babeanu S, et al. The Prevention of Dementia With Antihypertensive Treatment. New Evidence From the Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst-Eur) Study. Archives of Internal Medicine 2002;162:2046-2052. - PubMed
-
- Forette F, Seux ML, Staessen JA, Thijs L, Birkenhager WH, Babarskiene MR, et al. Prevention of dementia in randomised double-blind placebo-controlled Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst-Eur) Trial. Lancet 1998;352:1347-51. - PubMed
Zhang 2018 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ji T, Zhao Y, Wang J, Cui Y, Duan D, Chai Q, et al. Effect of low dose statins and apolipoprotein E genotype on cerebral small vessel disease in older hypertensive patients: a subgroup analysis of a randomized clinical trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2018;19:995-1002. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H, Cui Y, Zhao Y, Dong Y, Duan D, Wang J, Sheng L, Ji T, Zhou T, Hu W, Chen Y, Sun S, Gong G, Chai Q, Liu Z. Effects of sartans and low-dose statins on cerebral white matter hyperintensities and cognitive function in older patients with hypertension: a randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled clinical trial. Hypertension research 2018;42(5):717-729. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
ADVANCE 2010 {published data only}
-
- ADVANCE Management Committee. Study rationale and design of ADVANCE: action in diabetes and vascular disease--preterax and diamicron MR controlled evaluation. Diabetologia 2001;44(9):1118-20. - PubMed
-
- Batty GD, Li Q, Huxley R, Zoungas S, Taylor BA, Neal B, et al, ADVANCE Collaborative group. Oral disease in relation to future risk of dementia and cognitive decline: prospective cohort study based on the Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diamicron Modified-Release Controlled Evaluation (ADVANCE) trial. European Psychiatry 2013;28(1):49-52. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ninomiya T, Zoungas S, Neal B, Woodward M, Patel A, Perkovic V, et al, ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Efficacy and safety of routine blood pressure lowering in older patients with diabetes: results from the ADVANCE trial. Journal of Hypertension 2010;28(6):1141-9. - PubMed
-
- Patel A, ADVANCE Collaborative Group, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Woodward M, et al. Effects of a fixed combination of perindopril and indapamide on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the ADVANCE trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007;370(9590):829-40. - PubMed
-
- Van der Leeuw J, Visseren FL, Woodward M, Zoungas S, Kengne AP, Van der Graaf Y, et al. Predicting the effects of blood pressure-lowering treatment on major cardiovascular events for individual patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: results from Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diamicron MR Controlled Evaluation. Hypertension 2015;65(1):115-21. - PubMed
ALLHAT 2003 {published data only}
-
- ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. Diuretic Versus Alpha-Blocker as First-Step Antihypertensive Therapy. Final Results From the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). Hypertension 2003;42:239-246. - PubMed
ASCOT 2005 {published data only}
-
- Dahlof B, Sever PS, Poulter NR, Wedel H, Beevers DG, Caulfield M, et al. Prevention of cardiovascular events with an antihypertensive regimen of amlodipine adding perindopril as required versus atenolol adding bendroflumethiazide as required, in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial-Blood Pressure Lowering Arm (ASCOT-BPLA): a multicentre randomized controlled trial. Lancet 2005;366:895-906. - PubMed
Black 2001 {published data only}
-
- Black HR, Elliott WJ, Weber MA, Frishman WH, Strom JA, Liebson PR, et al. One-Year Study of Felodipine or Placebo for Stage 1 Isolated Systolic Hypertension. Hypertension 2001;38:1118-1130. - PubMed
Croog 1986 {published data only}
-
- Croog SH, Levine S, Testa MA, Brown B, Bulpitt CJ, Jenkins CD, et al. The effects of antihypertensive therapy on the quality of life. New England Journal of Medicine 1986;314(26):1657-64. - PubMed
DANTE 2015 {published data only}
-
- Moonen JE, Foster-Dingley JC, Ruijter W, Grond J, Bertens AS, Buchem MA, et al. Effect of Discontinuation of Antihypertensive Treatment in Elderly People on Cognitive Functioning--the DANTE Study Leiden: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Internal Medicine 2015;175(10):1622-30. - PubMed
Efimova 2014 {published data only}
Efimova 2015 {published data only}
-
- Efimova NY, Chernov VI, Efimova IY, Lishmanov YB. Influence of antihypertensive therapy on cerebral perfusion in patients with metabolic syndrome: relationship with cognitive function and 24-h arterial blood pressure monitoring. Cardiovascular Therapeutics 2015;33(4):209-15. - PubMed
ESH CHL SHOT {published data only}
-
- Zanchetti A, Liu L, Mancia G, Parati G, Grassi G, Stramba-Badiale M, et al, ESH-CHL-SHOT trial investigators. Continuation of the ESH-CHL-SHOT trial after publication of the SPRINT: rationale for further study on blood pressure targets of antihypertensive treatment after stroke. Journal Of Hypertension 2016;34(3):393-6. - PubMed
-
- Zanchetti A, Liu L, Mancia G, Parati G, Grassi G, Stramba-Badiale M, et al. Blood pressure and LDL-cholesterol targets for prevention of recurrent strokes and cognitive decline in the hypertensive patient: design of the European Society of Hypertension-Chinese Hypertension League Stroke in Hypertension Optimal Treatment randomized trial. Journal of Hypertension 2014;32:1888-97. - PubMed
EWPHE 1985 {published data only}
-
- Amery A, Birkenhäger W, Brixko P, Bulpitt C, Clement D, Leeuw P, et al. Influence of hypotensive drug treatment in elderly hypertensives: study terminating events in the trial of the European Working Party on High Blood Pressure in the Elderly. Journal of Hypertension. Supplement 1985;3(3):S501-11. - PubMed
FINGER 2015 {published data only}
-
- Kivipelto M, Solomon A, Ahtiluoto S, Ngandu T, Lehtisalo J, Antikainen R, et al. The Finnish Geriatric Intervention Study to Prevent Cognitive Impairment and Disability (FINGER) study. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2013 Nov;9(6):657-65. - PubMed
-
- Ngandu T, Lehtisalo J, Solomon A, Levälahti E, Ahtiluoto S, Antikainen R, et al. A 2 year multidomain intervention of diet, exercise, cognitive training, and vascular risk monitoring versus control to prevent cognitive decline in at-risk elderly people (FINGER): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015;385(9984):2255-63. - PubMed
Fogari 2003 {published data only}
-
- Fogari R, Mugellini A, Zoppi A, Derosa G, Pasotti C, Fogari E, et al. Influence of losartan and atenolol on memory function in very elderly hypertensive patients. Journal Of Human Hypertension 2003;17(11):781-5. - PubMed
Fogari 2006 {published data only}
-
- Fogari R, Mugellini A, Zoppi A, Lazzari P, Destro M, Rinaldi A, et al. Effect of telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide vs lisinopril/hydrochlorothiazide combination on ambulatory blood pressure and cognitive function in elderly hypertensive patients. Journal Of Human Hypertension 2006;20(3):177-85. - PubMed
Goldstein 1990 {published data only}
-
- Goldstein G, Materson BJ, Cushman WC, Reda DJ, Freis ED, Ramirez EA, et al. Treatment of hypertension in the elderly: II. Cognitive and behavioral function. Results of a Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study. Hypertension 1990;15(4):361-9. - PubMed
-
- Materson BJ, Cushman WC, Goldstein G, Reda DJ, Freis ED, Ramirez EA, et al. Treatment of hypertension in the elderly: I. Blood pressure and clinical changes. Results of a Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study. Hypertension 1990;15(4):348-60. - PubMed
HEART 2018 {published data only}
HOPE 3 2016 {published data only}
-
- Lonn E, Bosch J, Pogue J, Avezum A, Chazova I, Dans A, et al, HOPE-3 Investigators. Novel Approaches in Primary Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: The HOPE-3 Trial Rationale, Design, and Participants' Baseline Characteristics. The Canadian Journal of Cardiology 2016;32(3):311-8. - PubMed
-
- Lonn EM, Bosch J, López-Jaramillo P, Zhu J, Liu L, Pais P, et al, HOPE-3 Investigators. Blood-Pressure Lowering in Intermediate-Risk Persons without Cardiovascular Disease. The New England Journal of Medicine 2016;374(21):2009-20. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Lonn E, Pais P, Bosch J, López-Jaramillo P, Zhu J, et al, HOPE-3 Investigators. Blood-Pressure and Cholesterol Lowering in Persons without Cardiovascular Disease. The New England Journal Of Medicine 2016;374(21):2032-43. - PubMed
HOT 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hansson L, Zanchetti A, Carruthers SG, Dahlöf B, Elmfeldt D, Julius S, et al. Effects of intensive blood-pressure lowering and low-dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomised trial. HOT Study Group. Lancet 1998;351(9118):1755-62. - PubMed
Hsieh 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hsieh M-H, Chan P, Sue Y-M, Liu J-C, Liang TH, Huang T-Y, et al. Efficacy and Tolerability of Oral Stevioside in Patients with Mild Essential Hypertension: A Two-Year, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Study. Clinical Therapeutics 2003;25:2797-2808. - PubMed
INFINITY 2019 {published data only}
Lasser 1989 {published data only}
-
- Lasser NL, Nash J, Lasser VI, Hamill SJ, Batey DM. Effects of antihypertensive therapy on blood pressure control, cognition and reactivity. A placebo-controlled comparison of prazosin, propranolol, and hydrochlorothiazide. Am J Med 1989;86:98-103. - PubMed
LOW BP VIENNA 2018 {published data only}
ONTARGET 2008 {published data only}
-
- Anderson C, Teo K, Gao P, Arima H, Dans A, Unger T, et al, ONTARGET and TRANSCEND Investigators. Renin-angiotensin system blockade and cognitive function in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease: analysis of data from the ONTARGET and TRANSCEND studies. Lancet Neurology 2011;10(1):43-53. - PubMed
-
- ONTARGET Investigators, Yusuf S, Teo KK, Pogue J, Dyal L, Copland I, et al. Telmisartan, ramipril, or both in patients at high risk for vascular events. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;358(15):1547-59. - PubMed
-
- Teo K, Yusuf S, Sleight P, Anderson C, Mookadam F, Ramos B, et al, ONTARGET/TRANSCEND Investigators. Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of 2 large, simple, randomized trials evaluating telmisartan, ramipril, and their combination in high-risk patients: the Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial/Telmisartan Randomized Assessment Study in ACE Intolerant Subjects with Cardiovascular Disease (ONTARGET/TRANSCEND) trials. American Heart Journal 2004;148(1):52-61. - PubMed
PreDIVA 2016 {published data only}
-
- Moll van Charante EP, Richard E, Eurelings LS, Dalen JW, Ligthart SA, Bussel EF, et al. Effectiveness of a 6-year multidomain vascular care intervention to prevent dementia (preDIVA): a cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016;388(10046):797-805. - PubMed
PRESERVE 2018 {published data only}
PRoFESS 2008 {published data only}
-
- Diener HC, Sacco RL, Yusuf S, Cotton D, Ounpuu S, Lawton WA, et al. Effects of aspirin plus extended-release dipyridamoleversus clopidogrel and telmisartan on disability and cognitive function after recurrent stroke in patients with ischaemic stroke in the Prevention Regimen for Effectively Avoiding Second Strokes (PRoFESS) trial: a double-blind, active and placebo-controlled study. Lancet Neurology 2008;7:875-84. - PMC - PubMed
PROGRESS 2003 {published data only}
-
- The PROGRESS Collaborative Group. Effects of Blood Pressure Lowering With Perindopril and Indapamide Therapy on Dementia and Cognitive Decline in Patients With Cerebrovascular Disease. Arch Intern Med 2003;163:1069-75. - PubMed
rrAD 2019 {published data only}
SPS3 2014 {published data only}
-
- Pearce LA, McClure LA, Anderson DC, Jacova C, Sharma M, Hart RG, et al. Effects of long-term blood pressure lowering and dual antiplatelet therapy on cognition in patients with recent lacunar stroke: Secondary Prevention of Small Subcortical Strokes (SPS3) trial. Lancet Neurology 2014;13(12):1177-85. - PMC - PubMed
Starr 1996 {published data only}
-
- Starr JM, Whalley LJ, Deary IJ. The effects of antihypertensive treatment on cognitive function: results from the HOPE study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1996;44(4):411-5. - PubMed
-
- Starr JM, Whalley LJ. Hypertensive Old People in Edinburgh (HOPE) Study: electrocardiographic changes after captopril or bendrofluazide treatment. Age and Ageing 1993;22(5):343-8. - PubMed
STOP 1991 {published data only}
-
- Dahlof B, Lindholm LH, Hansson L, Schersten B, Ekbom T, Wester P-O. Morbidity and mortality in the Swedish Trial in Old Patients with Hypertension (STOP Hypertension). Lancet 1991;338:1281-85. - PubMed
Syst China 1998 {published data only}
-
- Liu L, Wang JG, Gong L, Liu G, Staessen JA. Comparison of active treatment and placebo in older Chinese patients with isolated systolic hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 1998;16:1823-1829. - PubMed
Tedesco 1999 {published data only}
-
- Tedesco MA, Ratti G, Mennella S, Manzo G, Grieco M, Rainone AC, et al. Comparison of losartan and hydrochlorothiazide on cognitive function and quality of life in hypertensive patients. American Journal Of Hypertension 1999;12((11 Pt 1)):1130-4. - PubMed
TRANSCEND 2008 {published data only}
-
- Telmisartan Randomised AssessmeNt Study in ACE iNtolerant subjects with cardiovascular Disease (TRANSCEND) Investigators, Yusuf S, Teo K, Anderson C, Pogue J, Dyal L, et al. Effects of the angiotensin-receptor blocker telmisartan on cardiovascular events in high-risk patientsintolerant to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2008;372(9644):1174-83. - PubMed
VALUE 2004 {published data only}
-
- Julius S, Kjeldsen SE, Weber M, Brunner HR, Ekman S, Hansson L, et al. Outcomes in hypertensive patients at high cardiovascular risk treated with regimens based on valsartan or amlodipine: the VALUE randomised trial. Lancet 2004;363:2022-31. - PubMed
Wei 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
Zheleznyh 2016 {published data only}
-
- Zheleznyh EA, Danilogorskaya YA, Privalova EV, Belenkov YN, Schendrygina AA, Pavlov NA, et al. Effect of Combined Antihypertensive Therapy With Perindopril and Indapamide on Morpho-Functional Parameters of The Heart, Blood Vessels of Small and Medium Caliber in Patients With Essential Hypertension. Kardiologiia 2016;56(3):19-24. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
CHIEF 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ma L, Lu P, Zhang Y, Meng X, Fan P, Ma L, et al. Effects of antihypertensive therapy on cognitive function and health-related quality of life in high-risk hypertensive patients. Journal of Hypertension. Conference: 27th Scientific Meeting of the International Society of Hypertension, ISH 2018;36(Suppl 3):e334-5.
-
- Ma L, Wang W, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Deng Q, Liu M, et al. Combination of amlodipine plus angiotensin receptor blocker or diuretics in high-risk hypertensive patients: a 96-week efficacy and safety study. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 2012;12(2):137-42. - PubMed
-
- Wang W, Ma LY, Liu MB, Deng Q, Zhang YQ, Li W, et al, CHIEF Cooperative Group. Effects of amlodipine plus telmisartan or amlodipine plus amiloride regimen on blood pressure control in hypertensive patients: preliminary report of Chinese Hypertension Intervention Efficacy (CHIEF) trial. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2009;37(8):701-7. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
CEREBRAL {published data only}
-
- Yamano S, Horii M, Takami T, Sakuma M, Morimoto T, Okada S, et al. Comparison between angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers on the risk of stroke recurrence and longitudinal progression of white matter lesions and silent brain infarcts on MRI (CEREBRAL study): rationale, design, and methodology. International Journal of Stroke 2015;10(3):452-6. - PubMed
ESPRIT {published data only}
-
- Effects of Intensive Systolic Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment in Reducing RIsk of Vascular evenTs (ESPRIT) Study (ESPRIT). Ongoing study. Starting date of trial not provided. Contact author for more information.
OPTIMAL DIABETES {published data only}
-
- Optimal Blood Pressure for the prevenTIon of Major vAscuLar Events in Patients With DIABETES Mellitus (OPTIMAL-DIABETES). Ongoing study. Starting date of trial not provided. Contact author for more information.
Additional references
Albert 2011
-
- Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, Dubois B, Feldman HH, Fox NC, et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011;7(3):270-9. - PMC - PubMed
Andrews 2019
APA 1987
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd revised edition. Washington DC: APA, 1987.
APA 1994
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th edition. Washington DC: APA, 1994.
Bar‐On 1993
-
- Bar-On D, Amir M. Reexamining the quality of life of hypertensive patients. A new self-structured measure. American Journal of Hypertension 1993;6(3 Pt 2):62S-66S. - PubMed
Birns 2009
-
- Birns J, Kalra L. Cognitive function and hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension 2009;23(2):86-96. - PubMed
Bohannon 2002
-
- Bohannon AD, Fillenbaum GG, Pieper CF, Hanlon JT, Blazer DG. Relationship of race/ethnicity and blood pressure to change in cognitive function. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2002;50(3):424-9. - PubMed
Brayne 1998
-
- Brayne C, Gill C, Huppert FA et al. Vascular risks and incident dementia:results from a cohort study of the very old. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 1998;9:175-180. - PubMed
Creavin 2016
-
- Creavin ST, Wisniewski S, Noel‐Storr AH, Trevelyan CM, Hampton T, Rayment D, et al. Mini‐Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the detection of dementia in clinically unevaluated people aged 65 and over in community and primary care populations. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, Issue 1. Art. No: CD011145. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011145.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Davis 2015
Degl'Innocenti 2004
-
- Degl'Innocenti A, Elmfeldt D, Hofman A, Lithell H, Olofsson B, Skoog I, et al. Health-related quality of life during treatment of elderly patients with hypertension: results from the Study on COgnition and Prognosis in the Elderly (SCOPE). Journal of Human Hypertension 2004;18(4):239-45. - PubMed
Di Bari 2001
-
- Di Bari M, Pahor M, Franse LV, Shorr RI, Wan JY, Ferrucci L, et al. Dementia and disability outcomes in large hypertension trials: lessons learned from the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP) trial. American Journal of Epidemiology 2001;153(1):72-8. - PubMed
Dubois 2007
-
- Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Dekosky ST, Barberger-Gateau P, Cummings J, et al. Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurology 2007;6(8):734-46. - PubMed
Elias 1993
-
- Elias MF, Wolf PA, Agostino RBD, Cobb J, White LR. Untreated blood pressure is inversely related to cognitive functioning: the Framingham Study. Journal of Epidemiology 1993;138(6):352-64. - PubMed
Elias 2004
-
- Elias PK, Elias MF, Robbins MA, Budge MM. Blood pressure related cognitive decline: does age make a difference? Hypertension 2004;44:631-636. - PubMed
Elias 2018
Fink 2018
-
- Fink HA, Jutkowitz E, McCarten JR, Hemmy LS, Butler M, Davila H, et al. Pharmacologic interventions to prevent cognitive decline, mild cognitive impairment, and clinical Alzheimer-type dementia: a systematic review. Annals of Internal Medicine 2018;168(1):39-51. - PubMed
Forette 2002
-
- Forette F, Seux M-L, Staessen JA, Thijs L, Babarskiene M-R, Babeanu S, et al. The prevention of dementia with antihypertensive treatment. New evidence from the Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst-Eur) Study. Archives of Internal Medicine 2002;162:2046-2052. - PubMed
Frankenhaeuser 1976
-
- Frankenhaeuser M, Gardell B. Underload and overload in working life: outline of a multidisciplinary approach. Journal of Human Stress 1976;2(3):35-46. - PubMed
Gorelick 2012
-
- Gorelick PB, Nyenhuis D, Materson BJ, Calhoun DA, Elliott WJ, Phillips RA, American Society of Hypertension Writing Group. Blood pressure and treatment of persons with hypertension as it relates to cognitive outcomes including executive function. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension : JASH 2012;6(5):309-15. - PubMed
Gottesman 2014
Guo 1996
Guo 1999
-
- Guo Z, Fratiglioni L, Zhu L, Fastborn J, Winblad B, Viitanen M. Occurence and progression of dementia in a community population aged 75 years and older: relationship of antihypertensive medication use. Archives of Neurology 1999;56:991-996. - PubMed
Gupta 2020
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Schunemann HJ, Tugwell P, Knottnerus A. GRADE guidelines: a new series of articles in the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):380-2. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hebert 2004
-
- Hebert LE, Scherr PA, Bennet DA, et al. Blood pressure and late-life cognitive function change: a biracial longitudinal population study. Neurology 2004;62:2021-2024. - PubMed
Howard 2012
-
- Howard R, McShane R, Lindesay J, Ritchie C, Baldwin A, Barber R, et al. Donepezil and memantine for moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. New England Journal of Medicine 2012;366(10):893-903. - PubMed
Hughes 2020
Iadecola 2016
-
- Iadecola C, Yaffe K, Biller J, Bratzke LC, Faraci FM, Gorelick PB, et al. American Heart Association Council on Hypertension; Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research; and Stroke Council. Hypertension 2016;68(6):e67-94.
JNC 7
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo Jr JL et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003;289(19):2560-72. - PubMed
JNC 8
-
- James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA 2014;311(5):507-20. - PubMed
Jones 2009
Jongstra 2016
Khachaturian 2006
-
- Khachaturian AS, Zandi PP, Lyketsos CG, Hayden KM, Skoog I, Norton MC, et al. Antihypertensive medication use and incident Alzheimer disease: the Cache County Study. Archives of Neurology 2006;63:686-92. - PubMed
Kilander 2000
-
- Kilander L, Nyman H, Boberg M, Lithell H. The association between low diastolic blood pressure in middle age and cognitive function in old age: a population based study. Age Ageing 2000;29:243-248. - PubMed
Kivipelto 2001
Larsson 2018
-
- Larsson SC, Markus HS. Does Treating Vascular Risk Factors Prevent Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Alzheimer's disease 2018;64(2):657-68. - PubMed
Launer 2000
-
- Launer LJ, Ross GW, Petrovich H, Masaki K, Foley D, White LR, et al. Midlife blood pressure and dementia: the Honolulu-Asia aging study. Neurobiology of Aging 2000;21:49-55. - PubMed
Levi Marpillat 2013
-
- Levi Marpillat N, Macquin-Mavier I, Tropeano AI, Bachoud-Levi AC, Maison P. Antihypertensive classes, cognitive decline and incidence of dementia: a network meta-analysis. Journal of Hypertension 2013;31(6):1073-82. - PubMed
Look AHEAD 2017
Lopez 2005
-
- Lopez OL, Becker JT, Saxton J, Sweet RA, Klunk W, DeKosky ST. Alteration of a Clinically Meaningful Outcome in the Natural History of Alzheimer's Disease by Cholinesterase Inhibition. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2005;53(1):83-7. - PubMed
McKhann 1984
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984;4:939-44. - PubMed
McKhann 2011
-
- McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR Jr, Kawas CH, et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2011;7(3):263-9. - PMC - PubMed
Morris 2001
-
- Morris MC, Scherr PA, Hebert LE, Glynn RJ, Bennett DA, Evans DA. Association of incident Alzheimer disease and blood pressure measured from 13 years before to 2 years after diagnosis in a large community study. Archives of Neurology 2001;58:1640-6. - PubMed
Murray 2017
-
- Murray AM, Hsu FC, Williamson JD, Bryan RN, Gerstein HC, Sullivan MD, et al, Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Follow-On Memory in Diabetes (ACCORDION MIND) Investigators. ACCORDION MIND: results of the observational extension of the ACCORD MIND randomised trial.. Diabetologia 2017;60(1):69-80. - PMC - PubMed
NICE 2019
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Hypertension in adults: diagnosis and management. Guideline 2019. - PubMed
O'Connor 2012
Pantoni 2005
-
- Pantoni L, Ser T, Soglian AG, Amigoni S, Spadari G, Binelli D, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nimodipine in Subcortical Vascular Dementia. Stroke 2005;36:619-24. - PubMed
Parsons 2016
-
- Parsons C, Murad MH, Andersen S, Mookadam F, Labonte H. The effect of antihypertensive treatment on the incidence of stroke and cognitive decline in the elderly: a meta-analysis. Future Cardiology 2016;12(2):237-48. - PubMed
Peters 2014
-
- Peters R, Booth A, Peters J. A systematic review of calcium channel blocker use and cognitive decline/dementia in the elderly. Journal of Hypertension 2014 Oct;32(10):1945-57. - PubMed
Peters 2018
-
- Peters R. INVESTIGATION OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVE CLASS EFFECTS ON DEMENTIA AND COGNITIVE DECLINE: A COLLABORATIVE META-ANALYSIS OF PARTICIPANT DATA. Alzheimers & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Associaiton July 2018;14(7):Supplement, Page P1388.
Peters 2019
-
- Peters R, Warwick J, Anstey KJ, Anderson CS. Blood pressure and dementia: What the SPRINT-MIND trial adds and what we still need to know. Neurology 2019;92(21):1017-8. - PubMed
Prince 2014
-
- Prince M, Albanese E, Guerchet M, Prina M. World Alzheimer Report 2014. Dementia and Risk Reduction: An Analysis Of Protective And Modifiable Factors. London: Alzheimer's Disease International, September 2014.
Qiu 2003
-
- Qiu C, Strauss E, Fastbom J, Winblad B, Fratiglioni L. Low blood pressure and risk of dementia in the Kungsholmen project: a 6-year follow-up study. Archives of Neurology 2003;60:223-8. - PubMed
Qiu 2003a
-
- Qiu C, Winblad B, Fastbom J, Fratiglioni L. Combined effects of APOE genotype, blood pressure and antihypertensive drug use on incident AD. Neurology 2003;61:655-60. - PubMed
Qiu 2004
-
- Qiu C, Strauss E, Winblad B, Fratiglioni L. Decline in blood pressure over time and risk of dementia: a longitudinal study from the Kungsholmen Project. Stroke 2004;35:1810-5. - PubMed
Reboussin 2018
-
- Reboussin DM, Allen NB, Griswold ME, Guallar E, Hong Y, Lackland DT, et al. Systematic Review for the 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2018;138(17):e595-616. - PubMed
Rouch 2015
-
- Rouch L, Cestac P, Hanon O, Cool C, Helmer C, Bouhanick B, et al. Antihypertensive drugs, prevention of cognitive decline and dementia: a systematic review of observational studies, randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses, with discussion of potential mechanisms. CNS Drugs 2015;29(2):113-30. - PubMed
Ruitenberg 2001
-
- Ruitenberg A, Skoog I, Ott A, Aevarsson O, Witteman JC, Lernfelt B, et al. Blood pressure and risk of dementia: results from the Rotterdam Study and the Gothenburg H-70 Study. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2001;12:33-9. - PubMed
Sharp 2011
-
- Sharp SI, Aarsland D, Day S, Sønnesyn H, Alzheimer's Society Vascular Dementia Systematic Review Group, Ballard C. Hypertension is a potential risk factor for vascular dementia: systematic review. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2011;26(7):661-9. - PubMed
Skoog 1996
-
- Skoog I, Lernfelt B, Landahl S, Palmertz B, Andreasson LA, Nilsson L, et al. 15-year longitudinal study of blood pressure and dementia. Lancet 1996;347(9009):1141-5. - PubMed
Swan 1998
-
- Swan GE, DeCarli C, Miller BL, Reed T, Wolf PA, Jack LM et al. Association of midlife blood pressure to late-life cognitive decline and brain morphology. Neurology 1998;51:986-93. - PubMed
Tervo 2004
-
- Tervo S, Kivipelto M, Hänninen T, Vanhanen M, Hallikainen M, Mannermaa A et al. Incidence and risk factors for mild cognitive impairment: a population based three-year follow-up study of cognitively healthy elderly subjects. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2004;17:196-203. - PubMed
Van Middelaar 2018
-
- Van Middelaar T, Van Vught LA, Van Gool WA, Simons EM, Van Den Born B-JH, Van Charante EP, et al. Blood pressure-lowering interventions to prevent dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Hypertension 2018;36(9):1780-7. - PubMed
Verghese 2003
-
- Verghese J, Lipton RB, Hall CB, Kuslansky G, Matz MJ. Low blood pressure and the risk of dementia in very old individuals. Neurology 2003;61:1667-72. - PubMed
Waldstein 2005
-
- Waldstein SR, Giggey PP, Thayer JF, Zonderman AB. Nonlinear relations of blood pressure to cognitive function: the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Hypertension 2005 Mar;45(3):374-9. - PubMed
Walker 2017
Wang 2003
-
- Wang JG, Staessen JA, Birkenhäger, WH. Antihypertensive treatment and prevention of stroke and dementia. Seminars in Cerebrovascular Diseases and Stroke 2003;3:155-64.
Warwick 2015
-
- Warwick J, Falaschetti E, Rockwood K, Mitnitski A, Thijs L, Beckett N, et al. No evidence that frailty modifies the positive impact of antihypertensive treatment in very elderly people: an investigation of the impact of frailty upon treatment effect in the HYpertension in the Very Elderly Trial (HYVET) study, a double-blind, placebo-controlled study of antihypertensives in people with hypertension aged 80 and over. BMC Medicine 2015;13:78. - PMC - PubMed
Weingartner 1983
-
- Weingartner H, Grafman J, Boutelle W, Kaye W, Martin PR. Forms of memory failure. Science 1983 Jul 22;221(4608):380-2. - PubMed
Weiss 2017
-
- Weiss J, Freeman M, Low A, Fu R, Kerfoot A, Paynter R, et al. Benefits and Harms of Intensive Blood Pressure Treatment in Adults Aged 60 Years or Older: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2017;166(6):419-29. - PubMed
Whelton 2018
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2018 Oct 23;138(17):e426-e483. - PubMed
Whitmer 2005
-
- Whitmer RA, Sidney S, Selby J, Johnston SC, Yaffe K. Midlife cardiovascular risk factors and risk of dementia in late life. Neurology 2005;64:277-81. - PubMed
WHO 1992
-
- World Health Organisation. The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders: clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines. Geneva: WHO, 1992.
Williams 2018
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, ESC Scientific Document Group. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. European Heart Journal 2018;39(33):3021-104. - PubMed
Wu 2003
-
- Wu C, Zhou D, Wen C, Zhang I, Como P, Qiao Y. Relationship between blood pressure and Alzheimer's disease in Linxian county. Life Science 2003;72:1125-33. - PubMed
Yamada 2003
-
- Yamada M, Kasagi F, Sasaki H, Maunari N, Mimori Y, Suzuki G. Association between dementia and midlife risk factors: the radiation effects research foundation adult health study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003;51:410-4. - PubMed
Yasar 2005
-
- Yasar S, Corrada M, Brookmeyer R, Kawas C. Calcium channel blockers and risk of AD: the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Neurobiology of Aging 2005;26:157-63. - PubMed
Yoshitake 1995
-
- Yoshitake T, Kiyohara Y, Kato I, Ohmura T, Iwamoto H, Nakayama K, et al. Incidence and risk factors of vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease in a defined elderly Japanese study: the Hisayama Study. Neurology 1995;45:1161-8. - PubMed
Zhuang 2016
-
- Zhuang S, Wang HF, Wang X, Li J, Xing CM. The association of renin-angiotensin system blockade use with the risks of cognitive impairment of aging and Alzheimer's disease: A meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2016;33:32-8. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
McGuinness 2006
-
- McGuinness B, Todd S, Passmore P, Bullock R. Blood pressure lowering in patients without prior cerebrovascular disease for prevention of cognitive impairment and dementia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 2. Art. No: CD004034. Art. No: CD004034. [DOI: CD004034. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004034.pub2] - PMC - PubMed
McGuinness 2009
-
- McGuinness B, Todd S, Passmore P, Bullock R. Blood pressure lowering in patients without prior cerebrovascular disease for prevention of cognitive impairment and dementia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 3. Art. No: CD004034. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004034.pub3] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

