Women's Initial Experiences and up to a Year in Retrospect of Their Life Situation With a Confirmed Takotsubo Syndrome Diagnosis: A Single Case Study Literature Review
- PMID: 34029129
- PMCID: PMC9121527
- DOI: 10.1177/08980101211018343
Women's Initial Experiences and up to a Year in Retrospect of Their Life Situation With a Confirmed Takotsubo Syndrome Diagnosis: A Single Case Study Literature Review
Erratum in
-
Correction Statement: Country Affiliations and Conflict of Interest Statements.J Holist Nurs. 2022 Sep;40(3):NP1-NP5. doi: 10.1177/08980101221127086. J Holist Nurs. 2022. PMID: 36398997 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
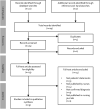
Purpose: To describe women's initial experiences and up to a year in retrospect of their life situation with a confirmed Takotsubo syndrome (TS) diagnosis. Method: A single case study literature review based on nine articles published by nurses was analyzed deductively using a nursing life dimension model. Results: All but one case was conducted on the North American continent and TS had largely affected women with previous cardiac history and had been triggered by one or two stressful life events. The biophysical life dimension manifested in distinct and troublesome inconvenience and in retrospect in fretting and grievous ailments. The emotional dimension manifested in pronounced ways and attitude-related sensations, feelings or moods while the intellectual dimension manifested in an unmanageable world of thought. The spiritual-existential dimension manifested in a life-denying view of life and the socio-cultural dimension manifested in an asocial life. Conclusions: With TS best practice in mind and a person-centered care and holistic approach, comprehensive descriptions are needed of how women identify, interpret, and use knowledge to manage their life situation. Cardiac nurses need further comprehensive descriptions to implement actions. Prior to implementation of such programs, this knowledge needs to be disseminated among cardiac nurses and evaluated in international randomized controlled trials.
Keywords: Takotsubo syndrome; case study; holistic nursing; person-centered care; qualitative method; stressful life events; women.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences (2002). International ethical guidelines for biomedical research involving human subjects. World Health Organization. http://www.cioms.ch/publications/guidelines/guidelines_nov_2002_blurb.htm - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources