Arginine methylation of SARS-Cov-2 nucleocapsid protein regulates RNA binding, its ability to suppress stress granule formation, and viral replication
- PMID: 34029587
- PMCID: PMC8141346
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100821
Arginine methylation of SARS-Cov-2 nucleocapsid protein regulates RNA binding, its ability to suppress stress granule formation, and viral replication
Abstract
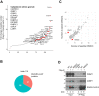
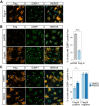
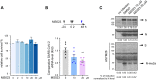
Viral proteins are known to be methylated by host protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) necessary for the viral life cycle, but it remains unknown whether severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) proteins are methylated. Herein, we show that PRMT1 methylates SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein at residues R95 and R177 within RGG/RG motifs, preferred PRMT target sequences. We confirmed arginine methylation of N protein by immunoblotting viral proteins extracted from SARS-CoV-2 virions isolated from cell culture. Type I PRMT inhibitor (MS023) or substitution of R95 or R177 with lysine inhibited interaction of N protein with the 5'-UTR of SARS-CoV-2 genomic RNA, a property required for viral packaging. We also defined the N protein interactome in HEK293 cells, which identified PRMT1 and many of its RGG/RG substrates, including the known interacting protein G3BP1 as well as other components of stress granules (SGs), which are part of the host antiviral response. Methylation of R95 regulated the ability of N protein to suppress the formation of SGs, as R95K substitution or MS023 treatment blocked N-mediated suppression of SGs. Also, the coexpression of methylarginine reader Tudor domain-containing protein 3 quenched N protein-mediated suppression of SGs in a dose-dependent manner. Finally, pretreatment of VeroE6 cells with MS023 significantly reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication. Because type I PRMT inhibitors are already undergoing clinical trials for cancer treatment, inhibiting arginine methylation to target the later stages of the viral life cycle such as viral genome packaging and assembly of virions may represent an additional therapeutic application of these drugs.
Keywords: PRMT1; RGG/RG motif; RNA binding; SARS-CoV-2; arginine methylation; condensate; nucleocapsid (N) protein; stress granules; type I PRMT inhibitor.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation in the Ser/Arg-rich region of the nucleocapsid of SARS-CoV-2 regulates phase separation by inhibiting self-association of a distant helix.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jun;300(6):107354. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107354. Epub 2024 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38718862 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 N protein coordinates viral particle assembly through multiple domains.J Virol. 2024 Nov 19;98(11):e0103624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01036-24. Epub 2024 Oct 16. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39412257 Free PMC article.
-
The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein forms mutually exclusive condensates with RNA and the membrane-associated M protein.Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 21;12(1):502. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20768-y. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33479198 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic Factors Behind Long COVID: VI. Combined Impact of G3BPs and SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein on the Viral Persistence and Long COVID.J Cell Biochem. 2025 May;126(5):e70038. doi: 10.1002/jcb.70038. J Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40415285 Review.
-
Phase separation by the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein: Consensus and open questions.J Biol Chem. 2022 Mar;298(3):101677. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101677. Epub 2022 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35131265 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering Plant Virus Species Forming Novel Provisional Taxonomic Units Related to the Family Benyviridae.Viruses. 2022 Nov 29;14(12):2680. doi: 10.3390/v14122680. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36560684 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay Between Coronavirus and Type I IFN Response.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 4;12:805472. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.805472. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35317429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 metabolism: Mechanisms and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2022 Aug 9;3(3):e157. doi: 10.1002/mco2.157. eCollection 2022 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 35958432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PRMT5/WDR77 complex restricts hepatitis E virus replication.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Jun 5;19(6):e1011434. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011434. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37276230 Free PMC article.
-
A viral assembly inhibitor blocks SARS-CoV-2 replication in airway epithelial cells.Commun Biol. 2024 Apr 22;7(1):486. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06130-8. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38649430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gordon D.E., Jang G.M., Bouhaddou M., Xu J., Obernier K., White K.M., O’Meara M.J., Rezelj V.V., Guo J.Z., Swaney D.L., Tummino T.A., Huttenhain R., Kaake R.M., Richards A.L., Tutuncuoglu B. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature. 2020;583:459–468. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

