The investigation of mRNA vaccines formulated in liposomes administrated in multiple routes against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 34029632
- PMCID: PMC8139338
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.05.024
The investigation of mRNA vaccines formulated in liposomes administrated in multiple routes against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
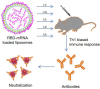
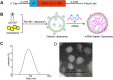
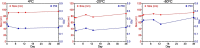
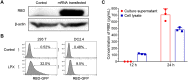
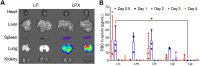
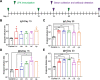
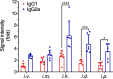
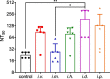
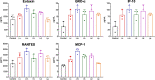
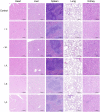
COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in an unprecedented global public health crisis. It is obvious that SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is needed to control the global COVID-19 public health crisis. Since obvious advantages including fast manufacturing speed, potent immunogenicity and good safety profile, six mRNA vaccines have been used to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infections in clinic with lipid nanoparticles (LNP) formulation via intramuscular injection. In this work, we first constructed RBD-encoding mRNA (RBD-mRNA) formulated in liposomes (LPX/RBD-mRNA) and investigated the influence of administration routes on the immunogenicity. LPX/RBD-mRNA can express RBD in vivo and successfully induced SARS-CoV-2 RBD specific antibodies in the vaccinated mice, which efficiently neutralized SARS-CoV-2 pseudotyped virus. Moreover, the administration routes were found to affect the virus neutralizing capacity of sera derived from the immunized mice and the types (Th1-type and Th2-type) of cellular immune responses. This study indicated that liposome-based RBD-mRNA vaccine with optimal administration route might be a potential candidate against SARS-CoV-2 infection with good efficacy and safety.
Keywords: Administration route; Liposomes; Receptor-binding domain; SARS-CoV-2; mRNA vaccines.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lurie N., Saville M., Hatchett R., Halton J. Developing Covid-19 vaccines at pandemic speed. 2020;382:1969–1973. - PubMed
-
- Le T.T., Cramer J.P., Chen R., Mayhew S. Evolution of the COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020;19:667–668. - PubMed
-
- Lu R., Zhao X., Li J., Niu P., Yang B., Wu H., Wang W., Song H., Huang B., Zhu N., Bi Y., Ma X., Zhan F., Wang L., Hu T., Zhou H., Hu Z., Zhou W., Zhao L., Chen J., Meng Y., Wang J., Lin Y., Yuan J., Xie Z., Ma J., Liu W.J., Wang D., Xu W., Holmes E.C., Gao G.F., Wu G., Chen W., Shi W., Tan W. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet. 2020;395:565–574. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

