Flavonoids, the Family of Plant-Derived Antioxidants Making Inroads into Novel Therapeutic Design Against Ionizing Radiation-Induced Oxidative Stress in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 34030619
- PMCID: PMC9413797
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X19666210524152817
Flavonoids, the Family of Plant-Derived Antioxidants Making Inroads into Novel Therapeutic Design Against Ionizing Radiation-Induced Oxidative Stress in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
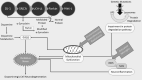
Background: Ionizing radiation from telluric sources is unceasingly an unprotected pitfall to humans. Thus, the foremost contributors to human exposure are global and medical radiations. Various evidences assembled during preceding years reveal the pertinent role of ionizing radiation- induced oxidative stress in the progression of neurodegenerative insults, such as Parkinson's disease, which have been contributing to increased proliferation and generation of reactive oxygen species.
Objective: This review delineates the role of ionizing radiation-induced oxidative stress in Parkinson's disease and proposes novel therapeutic interventions of flavonoid family, offering effective management and slowing down the progression of Parkinson's disease.
Methods: Published papers were searched in MEDLINE, PubMed, etc., published to date for indepth database collection.
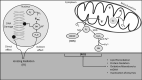
Results: The oxidative damage may harm the non-targeted cells. It can also modulate the functions of the central nervous system, such as protein misfolding, mitochondria dysfunction, increased levels of oxidized lipids, and dopaminergic cell death, which accelerate the progression of Parkinson's disease at the molecular, cellular, or tissue levels. In Parkinson's disease, reactive oxygen species exacerbate the production of nitric oxides and superoxides by activated microglia, rendering death of dopaminergic neuronal cell through different mechanisms.
Conclusion: Rising interest has extensively engrossed in the clinical trial designs based on the plant-derived family of antioxidants. They are known to exert multifarious impact on neuroprotection via directly suppressing ionizing radiation-induced oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species production or indirectly increasing the dopamine levels and activating the glial cells.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; ROS; antioxidants; flavonoids; ionizing radiation; oxidative stress.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective Mechanisms of Flavonoids in Parkinson's Disease.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:314560. doi: 10.1155/2015/314560. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26576219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants for treatment of Parkinson's disease: preclinical and clinical outcomes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1842(8):1282-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.09.007. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24060637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Flavonoids in Protecting Against Neurodegenerative Diseases-Possible Mechanisms of Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 16;26(10):4763. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104763. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combating Parkinson's disease with plant-derived polyphenols: Targeting oxidative stress and neuroinflammation.Neurochem Int. 2024 Sep;178:105798. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105798. Epub 2024 Jun 29. Neurochem Int. 2024. PMID: 38950626 Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and Dopaminergic Metabolism: A Major PD Pathogenic Mechanism and Basis of Potential Antioxidant Therapies.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;23(7):852-864. doi: 10.2174/1871527322666230609141519. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37303175 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear Factor Kappa B: A Nobel Therapeutic Target of FlavonoidsAgainst Parkinson's Disease.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(14):2062-2077. doi: 10.2174/0113862073295568240105025006. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 38243959 Review.
-
Uncovering the pharmacology of Ginkgo biloba folium in the cell-type-specific targets of Parkinson's disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 29;13:1007556. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1007556. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36249800 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Oxidative Stress, Selenium, and Cumulative Risk in Metabolic Syndrome.In Vivo. 2023 Nov-Dec;37(6):2877-2887. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13406. In Vivo. 2023. PMID: 37905638 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study of Diospyros malabarica (Gaub) Extracts in Various Polarity-Dependent Solvents for Evaluation of Phytoconstituents and Biological Activities.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jun 25;2022:4746223. doi: 10.1155/2022/4746223. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35789643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harada K.H., Niisoe T., Imanaka M., Takahashi T., Amako K., Fujii Y., Kanameishi M., Ohse K., Nakai Y., Nishikawa T., Saito Y., Sakamoto H., Ueyama K., Hisaki K., Ohara E., Inoue T., Yamamoto K., Matsuoka Y., Ohata H., Toshima K., Okada A., Sato H., Kuwamori T., Tani H., Suzuki R., Kashikura M., Nezu M., Miyachi Y., Arai F., Kuwamori M., Harada S., Ohmori A., Ishikawa H., Koizumi A. Radiation dose rates now and in the future for residents neighboring restricted areas of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111(10):E914–E923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315684111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hall E.J., Giaccia A.J. Radiobiology for the Radiologist. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006.
-
- Mapuskar K.A., Anderson C.M., Spitz D.R., Batinic-Haberle I., Allen B.G.E., Oberley-Deegan R. Utilizing superoxide dismutase mimetics to enhance radiation therapy response while protecting normal tissues. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2019;29(1):72–80. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2018.10.005. https://dpi.org/10.1016/j.semradonc.2018.10.005 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical