A new mouse SNP genotyping assay for speed congenics: combining flexibility, affordability, and power
- PMID: 34030629
- PMCID: PMC8142480
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-021-07698-9
A new mouse SNP genotyping assay for speed congenics: combining flexibility, affordability, and power
Abstract
Background: Speed congenics is an important tool for creating congenic mice to investigate gene functions, but current SNP genotyping methods for speed congenics are expensive. These methods usually rely on chip or array technologies, and a different assay must be developed for each backcross strain combination. "Next generation" high throughput DNA sequencing technologies have the potential to decrease cost and increase flexibility and power of speed congenics, but thus far have not been utilized for this purpose.
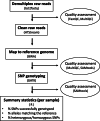
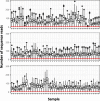
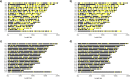
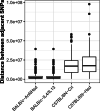
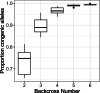
Results: We took advantage of the power of high throughput sequencing technologies to develop a cost-effective, high-density SNP genotyping assay that can be used across many combinations of backcross strains. The assay surveys 1640 genome-wide SNPs known to be polymorphic across > 100 mouse strains, with an expected average of 549 ± 136 SD diagnostic SNPs between each pair of strains. We demonstrated that the assay has a high density of diagnostic SNPs for backcrossing the BALB/c strain into the C57BL/6J strain (807-819 SNPs), and a sufficient density of diagnostic SNPs for backcrossing the closely related substrains C57BL/6N and C57BL/6J (123-139 SNPs). Furthermore, the assay can easily be modified to include additional diagnostic SNPs for backcrossing other closely related substrains. We also developed a bioinformatic pipeline for SNP genotyping and calculating the percentage of alleles that match the backcross recipient strain for each sample; this information can be used to guide the selection of individuals for the next backcross, and to assess whether individuals have become congenic. We demonstrated the effectiveness of the assay and bioinformatic pipeline with a backcross experiment of BALB/c-IL4/IL13 into C57BL/6J; after six generations of backcrosses, offspring were up to 99.8% congenic.
Conclusions: The SNP genotyping assay and bioinformatic pipeline developed here present a valuable tool for increasing the power and decreasing the cost of many studies that depend on speed congenics. The assay is highly flexible and can be used for combinations of strains that are commonly used for speed congenics. The assay could also be used for other techniques including QTL mapping, standard F2 crosses, ancestry analysis, and forensics.
Keywords: Allegro targeted genotyping; Bioinformatic pipeline; Illumina; Next generation sequencing; Single primer enrichment technology; Speed congenics.
Conflict of interest statement
KRA, DDN, and MWF are employed at the University of Idaho IBEST Genomics Resources Core facility, which offers the SNP genotyping assay described here (laboratory work and bioinformatic analysis) as a paid service to academic and commercial entities.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

