Serum checkpoint molecules in patients with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD)
- PMID: 34030721
- PMCID: PMC8142499
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-021-02527-6
Serum checkpoint molecules in patients with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD)
Abstract
Background: Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is characterized by increased serum IgG4 concentration and infiltration of IgG4+ plasma cells in the affected organs. The present study aimed to characterize the serum levels of coinhibitory checkpoint molecule, T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-containing-molecule-3 (TIM-3), and its ligand, galectin-9 (Gal-9), among IgG4-related disease in patients with IgG4-RD patients with various organ involvements.
Methods: Serum samples were collected from untreated 59 patients with IgG4-RD, 13 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and 37 healthy controls (HCs). HCs lacked chronic medical diseases or conditions and did not take prescription medications or over-the-counter medications within 7 days. Patients with IgG4-RD (n = 57) were subdivided into those with visceral involvement (n = 38) and those without visceral involvement (n = 21). Serum levels of Gal-9 and soluble TIM-3 (sTIM-3) were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The results were compared with the clinical phenotypes of IgG4-RD.
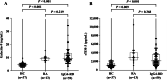
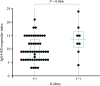
Results: In untreated patients with IgG4-RD, serum levels of Gal-9 and sTIM-3 were significantly higher than in RA patients as well as in healthy controls. There were significant correlations between the serum levels of Gal-9 or sTIM-3 and serum levels of IgG, BAFF, or sIL-2R. However, there was no significant correlation between the serum levels of Gal-9 or sTIM-3 and serum IgG4 concentrations. Serum levels of sTIM-3 were significantly higher in a subset of patients with visceral involvements than in those without visceral involvements. However, there was no significant difference in the serum levels of Gal-9 between IgG4-RD patients with and without visceral involvements, although both Gal-9 and sTIM-3 were elevated in untreated IgG4-RD patients, and the levels of these checkpoint molecules remained unchanged after steroid therapy.
Conclusion: Serum levels of Gal-9 and sTIM-3 were significantly elevated in untreated patients with IgG4-RD. Furthermore, serum levels of sTIM-3 were significantly higher in IgG4-RD patients with visceral involvements. These checkpoint molecules could be a potentially useful biomarker for IgG4-RD and for assessing the clinical phenotypes of IgG4-RD.
Keywords: Galectin-9; IgG4-related disease; Immune checkpoint molecules; T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-containing-molecule-3.
Conflict of interest statement
KM has received research grants from Chugai, Pfizer, and AbbVie. The rest of the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Elevated serum levels of checkpoint molecules in patients with adult Still's disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Jul 22;22(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02263-3. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32698838 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Levels of T Cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin-Domain Containing Molecule 3 in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.J Clin Med. 2020 Nov 5;9(11):3563. doi: 10.3390/jcm9113563. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33167436 Free PMC article.
-
Association between inflammatory cytokines and immune-checkpoint molecule in rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 18;16(11):e0260254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260254. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34793561 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Comparison with Sjögren's syndrome.Mod Rheumatol. 2020 Jan;30(1):7-16. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2019.1650694. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Mod Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31425659 Review.
-
Immunoglobulin G4-related hepatobiliary disease.Semin Diagn Pathol. 2019 Nov;36(6):423-433. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31358425 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Performance of Immunonephelometric Assay and Chemiluminescent Immunoassay for Detection of IgG Subclasses in Chinese.J Clin Lab Anal. 2024 Apr;38(8):e25033. doi: 10.1002/jcla.25033. Epub 2024 Apr 2. J Clin Lab Anal. 2024. PMID: 38563457 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-9 Regulates Monosodium Urate Crystal-Induced Gouty Inflammation Through the Modulation of Treg/Th17 Ratio.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 28;12:762016. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.762016. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34777378 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features and relapse risks factors of IgG4 related disease: a single-center retrospective study.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Nov;23(7):3527-3538. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01123-z. Epub 2023 Jul 1. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37392248
References
-
- Yamada K, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, Mizushima I, Matsui S, Fujisawa Y, Hara S, Takahashi H, Nomura H, Kawa S, Kawano M. New clues to the nature of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: a retrospective Japanese multicenter study of baseline clinical features of 334 cases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1467-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M, Mahajan VS, Della Torre E, Lee H, Kulikova M, Deshpande V, Pillai S, Stone JH. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(1):190–195. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205233. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

