Infection Prevention in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- PMID: 34030822
- PMCID: PMC8162277
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clp.2021.03.011
Infection Prevention in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Abstract
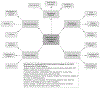
Although many aspects of infection prevention and control (IPC) mirror institutional efforts, optimization of IPC practices in the neonatal intensive care unit requires careful consideration of its unique population and environment, addressed here for key IPC domains. In addition, innovative mitigation efforts to address challenges specific to limited resource settings are discussed.
Keywords: Central line–associated bloodstream infections; Disinfection; Environmental cleaning; Health care–associated infections; Low- and middle-income countries.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Strengthening neonatal care through ward assistants: a Kenyan case study in enhancing infection prevention and control practices.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2025 Jun 2;14(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13756-025-01575-w. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2025. PMID: 40457467 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives and practices of healthcare providers and caregivers on healthcare-associated infections in the neonatal intensive care units of two hospitals in Ghana.Health Policy Plan. 2020 Nov 1;35(Supplement_1):i38-i50. doi: 10.1093/heapol/czaa102. Health Policy Plan. 2020. PMID: 33165583 Free PMC article.
-
Infection prevention and control practices of non-medical individuals in a neonatal intensive care unit: A Donabedian approach.Midwifery. 2022 Sep;112:103393. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2022.103393. Epub 2022 Jun 2. Midwifery. 2022. PMID: 35688023
-
Implementation of infection prevention and control for hospitalized neonates: A narrative review.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2024 Jan;30(1):44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2022.11.007. Epub 2022 Nov 19. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2024. PMID: 36414203 Review.
-
Recent trends and prevention of infection in the neonatal intensive care unit.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008 Aug;21(4):350-6. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e3283013af4. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18594285 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of a novel reprocessed bCPAP system on sepsis rates among preterm neonates with respiratory distress: a randomized controlled trial.Front Pediatr. 2025 May 19;13:1569437. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1569437. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40458453 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing infections from central lines in a neonatal intensive care unit, Egypt.Bull World Health Organ. 2025 May 1;103(5):343-348. doi: 10.2471/BLT.24.291949. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Bull World Health Organ. 2025. PMID: 40342848 Free PMC article.
-
Micafungin versus Amphotericin B in treatment of invasive fungal infection in preterm neonates: a randomized control trial.Ital J Pediatr. 2025 Feb 27;51(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13052-025-01852-9. Ital J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40016807 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Assessing Global Nursing Interventions in Reducing Hospital-Acquired Infections: A Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2025 May;54(5):915-927. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v54i5.18627. Iran J Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40765793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nosocomial infections in the surgical intensive care unit: an observational retrospective study from a large tertiary hospital in Palestine.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Oct 13;23(1):686. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08677-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37833675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Adams-Chapman I, et al. Neurodevelopmental and growth impairment among extremely low-birth-weight infants with neonatal infection. Jama. 2004;292(19):2357–2365. - PubMed
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen N, Fanaroff AA, et al. Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: the experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2002;110(2 Pt 1):285–291. - PubMed
-
- Patrick SW, Kawai AT, Kleinman K, et al. Health care-associated infections among critically ill children in the US, 2007-2012. Pediatrics. 2014;134(4):705–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

