The KDM4B-CCAR1-MED1 axis is a critical regulator of osteoclast differentiation and bone homeostasis
- PMID: 34031372
- PMCID: PMC8144413
- DOI: 10.1038/s41413-021-00145-1
The KDM4B-CCAR1-MED1 axis is a critical regulator of osteoclast differentiation and bone homeostasis
Abstract
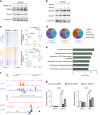
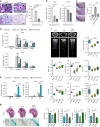
Bone undergoes a constant and continuous remodeling process that is tightly regulated by the coordinated and sequential actions of bone-resorbing osteoclasts and bone-forming osteoblasts. Recent studies have shown that histone demethylases are implicated in osteoblastogenesis; however, little is known about the role of histone demethylases in osteoclast formation. Here, we identified KDM4B as an epigenetic regulator of osteoclast differentiation. Knockdown of KDM4B significantly blocked the formation of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-positive multinucleated cells. Mice with myeloid-specific conditional knockout of KDM4B showed an osteopetrotic phenotype due to osteoclast deficiency. Biochemical analysis revealed that KDM4B physically and functionally associates with CCAR1 and MED1 in a complex. Using genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-sequencing, we revealed that the KDM4B-CCAR1-MED1 complex is localized to the promoters of several osteoclast-related genes upon receptor activator of NF-κB ligand stimulation. We demonstrated that the KDM4B-CCAR1-MED1 signaling axis induces changes in chromatin structure (euchromatinization) near the promoters of osteoclast-related genes through H3K9 demethylation, leading to NF-κB p65 recruitment via a direct interaction between KDM4B and p65. Finally, small molecule inhibition of KDM4B activity impeded bone loss in an ovariectomized mouse model. Taken together, our findings establish KDM4B as a critical regulator of osteoclastogenesis, providing a potential therapeutic target for osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

