Clinical utility of DaTscan in patients with suspected Parkinsonian syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34031400
- PMCID: PMC8144619
- DOI: 10.1038/s41531-021-00185-8
Clinical utility of DaTscan in patients with suspected Parkinsonian syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
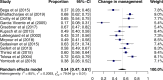
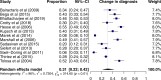
Images of DaTscan (ioflupane [123I] SPECT) have been used as an adjunct to clinical diagnosis to facilitate the differential diagnosis of neurodegenerative (ND) Parkinsonian Syndrome (PS) vs. non-dopamine deficiency aetiologies of Parkinsonism. Despite several systematic reviews having summarised the evidence on diagnostic accuracy, the impact of imaging results on clinical utility has not been systematically assessed. Our objective was to examine the available evidence on the clinical utility of DaTscan imaging in changing diagnosis and subsequent management of patients with suspected PS. We performed a systematic review of published studies of clinical utility from 2000 to 2019 without language restrictions. A meta-analysis of change in diagnosis and management rates reported from each study was performed using a random-effects model and logit transformation. Sub-group analysis, meta-regression and sensitivity analysis was performed to explore heterogeneity. Twenty studies met the inclusion criteria. Thirteen of these contributed to the meta-analyses including 950 and 779 patients with a reported change in management and change in diagnosis, respectively. The use of DaTscan imaging resulted in a change in management in 54% (95% CI: 47-61%) of patients. Change in diagnosis occurred in 31% (95% CI: 22-42%) of patients. The two pooled analyses were characterised by high levels of heterogeneity. Our systematic review and meta-analysis show that imaging with DaTscan was associated with a change in management in approximately half the patients tested and the diagnosis was modified in one third. Regardless of time from symptom onset to scan results, these changes were consistent. Further research focusing on specific patient subgroups could provide additional evidence on the impact on clinical outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: A.C., T.M. and M.G. received funding for this analysis from GE Healthcare and are employees of Kings College London. D.B., P.K. and A.A. have acted as consultants for GE Healthcare. P.K. has acted as a consultant, speaker and grant recipient for GE Healthcare and is an employee of Konica-Minolta. A.A. has received compensation for consultancy and speaker-related activities from UCB, Boehringer–Ingelheim, General Electric, Britannia, AbbVie, Kyowa Kirin, Zambon, Bial, Neuroderm, Theravance Biopharma, Roche; he receives research support from Chiesi Pharmaceuticals, Bial, Lundbeck, Horizon2020 - Grant 825785, Horizon2020 Grant 101016902, Ministry of Education University and Research (MIUR) Grant ARS01_01081, Cariparo Foundation. He serves as a consultant for Boehringer–Ingelheim for legal cases on pathological gambling. Z.H. and C.B. are employees of GE Healthcare.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

