COVID-19 diagnosis by routine blood tests using machine learning
- PMID: 34031483
- PMCID: PMC8144373
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90265-9
COVID-19 diagnosis by routine blood tests using machine learning
Abstract
Physicians taking care of patients with COVID-19 have described different changes in routine blood parameters. However, these changes hinder them from performing COVID-19 diagnoses. We constructed a machine learning model for COVID-19 diagnosis that was based and cross-validated on the routine blood tests of 5333 patients with various bacterial and viral infections, and 160 COVID-19-positive patients. We selected the operational ROC point at a sensitivity of 81.9% and a specificity of 97.9%. The cross-validated AUC was 0.97. The five most useful routine blood parameters for COVID-19 diagnosis according to the feature importance scoring of the XGBoost algorithm were: MCHC, eosinophil count, albumin, INR, and prothrombin activity percentage. t-SNE visualization showed that the blood parameters of the patients with a severe COVID-19 course are more like the parameters of a bacterial than a viral infection. The reported diagnostic accuracy is at least comparable and probably complementary to RT-PCR and chest CT studies. Patients with fever, cough, myalgia, and other symptoms can now have initial routine blood tests assessed by our diagnostic tool. All patients with a positive COVID-19 prediction would then undergo standard RT-PCR studies to confirm the diagnosis. We believe that our results represent a significant contribution to improvements in COVID-19 diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Marko Notar is the CEO of Smart Blood Analytics SA. Matjaž Kukar, Gregor Gunčar, and Mateja Notar are Smart Blood Analytics advisors, and other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
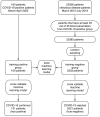
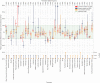

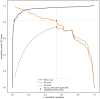
References
-
- World health organization. WHO Director-General’s remarks at the media briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11 February 2020. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-remarks-at... (2020).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

