Molecular basis of the new COVID-19 target neuropilin-1 in complex with SARS-CoV-2 S1 C-end rule peptide and small-molecule antagonists
- PMID: 34031621
- PMCID: PMC8133821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116537
Molecular basis of the new COVID-19 target neuropilin-1 in complex with SARS-CoV-2 S1 C-end rule peptide and small-molecule antagonists
Abstract
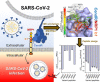
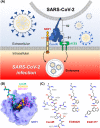
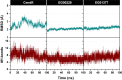
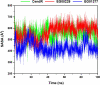
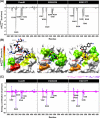
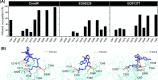
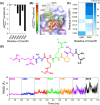
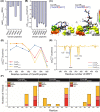
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), responsible for causing the current coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, uses its spike (S1) protein for host cell attachment and entry. Apart from angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, neuropilin-1 (NRP1) has been recently found to serve as another host factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection; thus, blocking S1-NRP1 interaction can be a potential treatment for COVID-19. Herein, molecular recognition between SARS-CoV-2 S1 C-end rule (CendR) heptapeptide including small-molecule antagonists (EG00229 and EG01377) and the NRP1 was investigated using molecular dynamics simulations and binding free energy calculations based on MM-PBSA method. The binding affinity and the number of hot-spot residues of EG01377/NRP1 complex were higher than those of CendR/NRP1 and EG00229/NRP1 systems, in line with the reported experimental data as well as with the lower water accessibility at the ligand-binding site. The (i) T316, P317, and D320 and (ii) S346, T349, and Y353 residues of NRP1 were confirmed to respectively form H-bonds with the positively charged guanidinium group and the negatively charged carboxyl moiety of all studied ligands. Moreover, Rosetta protein design was employed to improve the binding affinity between CendR peptide and NRP1. The newly designed peptides, especially R683G and A684M, exhibited higher binding efficiency than the native CendR heptapeptide as well as the small-molecule EG00229 by forming more H-bonds and hydrophobic interactions with NPR1, suggesting that these designed peptides could be promising NRP1 inhibitors to combat SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; EG00229; EG01377; Neuropilin-1; SARS-CoV-2 S1 CendR.
© 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Binding to Neuropilin 1.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 28;15(2):165. doi: 10.3390/ph15020165. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215277 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of peptide binding to the SARS-CoV-2 host factor neuropilin.Heliyon. 2021 Oct;7(10):e08251. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08251. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34722943 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropilin-1 assists SARS-CoV-2 infection by stimulating the separation of Spike protein S1 and S2.Biophys J. 2021 Jul 20;120(14):2828-2837. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.05.026. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Biophys J. 2021. PMID: 34087218 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropilin 1: A Novel Entry Factor for SARS-CoV-2 Infection and a Potential Therapeutic Target.Biologics. 2021 May 6;15:143-152. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S307352. eCollection 2021. Biologics. 2021. PMID: 33986591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropilins: C-end rule peptides and their association with nociception and COVID-19.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:1889-1895. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.03.025. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33815686 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Energy- and evolution-based design of inulosucrase for enhanced thermostability and inulin production.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Nov;107(22):6831-6843. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12759-y. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37688600
-
Enhancing solubility and stability of sorafenib through cyclodextrin-based inclusion complexation: in silico and in vitro studies.RSC Adv. 2023 Sep 11;13(39):27244-27254. doi: 10.1039/d3ra03867j. eCollection 2023 Sep 8. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37701271 Free PMC article.
-
Machine-learning-assisted high-throughput identification of potent and stable neutralizing antibodies against all four dengue virus serotypes.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 26;14(1):17165. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67487-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39060292 Free PMC article.
-
Quinoxalinones as A Novel Inhibitor Scaffold for EGFR (L858R/T790M/C797S) Tyrosine Kinase: Molecular Docking, Biological Evaluations, and Computational Insights.Molecules. 2022 Dec 14;27(24):8901. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248901. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36558033 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropilin-1 in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia, HIV-1, and SARS-CoV-2 infection: A review.Virus Res. 2022 Oct 2;319:198880. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2022.198880. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Virus Res. 2022. PMID: 35905790 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nutho B., Mahalapbutr P., Hengphasatporn K., Pattaranggoon N.C., Simanon N., Shigeta Y., Hannongbua S., Rungrotmongkol T. Biochemistry. 2020;59:1769. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
