From Quinoline to Quinazoline-Based S. aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors by Coupling a Focused Scaffold Hopping Approach and a Pharmacophore Search
- PMID: 34032014
- PMCID: PMC8518402
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202100282
From Quinoline to Quinazoline-Based S. aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors by Coupling a Focused Scaffold Hopping Approach and a Pharmacophore Search
Abstract
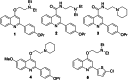
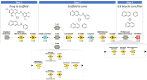
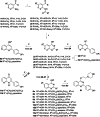
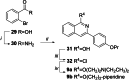
Antibiotic resistance breakers, such as efflux pump inhibitors (EPIs), represent a powerful alternative to the development of new antimicrobials. Recently, by using previously described EPIs, we developed pharmacophore models able to identify inhibitors of NorA, the most studied efflux pump of Staphylococcus aureus. Herein we report the pharmacophore-based virtual screening of a library of new potential NorA EPIs generated by an in-silico scaffold hopping approach of the quinoline core. After chemical synthesis and biological evaluation of the best virtual hits, we found the quinazoline core as the best performing scaffold. Accordingly, we designed and synthesized a series of functionalized 2-arylquinazolines, which were further evaluated as NorA EPIs. Four of them exhibited a strong synergism with ciprofloxacin and a good inhibition of ethidium bromide efflux on resistant S. aureus strains coupled with low cytotoxicity against human cell lines, thus highlighting a promising safety profile.
Keywords: NorA efflux pump inhibitors; Staphylococcus aureus; antibiotics; medicinal chemistry; quinazoline derivatives.
© 2021 The Authors. ChemMedChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural Modifications of the Quinolin-4-yloxy Core to Obtain New Staphylococcus aureus NorA Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 24;21(19):7037. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197037. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32987835 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on 2-phenylquinoline Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors: New insights on the C-6 position.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jul 15;155:428-433. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.06.013. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29908437
-
C-2 phenyl replacements to obtain potent quinoline-based Staphylococcus aureus NorA inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020 Dec;35(1):584-597. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1719083. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31992093 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on Staphylococcus aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(24):2168-2185. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200704135837. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32621719 Review.
-
Tackling multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by natural products and their analogues acting as NorA efflux pump inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2023 Feb 15;80:117187. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2023.117187. Epub 2023 Jan 27. Bioorg Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36731248 Review.
Cited by
-
NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors: Expanding SAR Knowledge of Pyrazolo[4,3-c][1,2]benzothiazine 5,5-Dioxide Derivatives.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025 May;358(5):e70000. doi: 10.1002/ardp.70000. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025. PMID: 40390184 Free PMC article.
-
Efflux Pump (QacA, QacB, and QacC) and β-Lactamase Inhibitors? An Evaluation of 1,8-Naphthyridines against Staphylococcus aureus Strains.Molecules. 2023 Feb 15;28(4):1819. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041819. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838807 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the potentiality of quinazoline derivatives against Pseudomonas aeruginosa with antimicrobial synergy and SAR analysis.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2024 Jun;77(6):365-381. doi: 10.1038/s41429-024-00717-3. Epub 2024 Mar 21. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2024. PMID: 38514856
-
Microbial Efflux Pump Inhibitors: A Journey around Quinoline and Indole Derivatives.Molecules. 2021 Nov 19;26(22):6996. doi: 10.3390/molecules26226996. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34834098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efflux, Signaling and Warfare in a Polymicrobial World.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Apr 8;12(4):731. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12040731. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107093 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO, Bull. W. H. O. 2014, 61, 383–94.
-
- Venter H., Biosci. Rep. 2019, 29, BSR2 0180474.
-
- Roope L. S. J., Smith R. D., Pouwels K. B., Buchanan J., Abel L., Eibich P., Butler C. C., Tan P. S., Walker A. S., Robotham J. V., et al., Science 2019, 364, 364. - PubMed
-
- Cassini A., Högberg L. D., Plachouras D., Quattrocchi A., Hoxha A., Simonsen G. S., Colomb-Cotinat M., Kretzschmar M. E., Devleesschauwer B., Cecchini M., et al., Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

