Uptake of Biosimilars and Its Economic Implication for the Treatment of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Korea
- PMID: 34032032
- PMCID: PMC8144596
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e143
Uptake of Biosimilars and Its Economic Implication for the Treatment of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Korea
Abstract
Background: We aimed to examine the uptake of infliximab and etanercept biosimilars in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and its economic implication for healthcare expenditure.
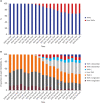
Methods: Using Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service National Patient Samples, we extracted RA patients who used biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) between 2009 and 2018. Descriptive statistics were used to explain the basic features of the data. We calculated the proportion of users of each bDMARD among total patients with bDMARDs half-yearly. We assessed changes in the utilization proportions of bDMARDs including 4 tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis) and 2 non-TNFis, which have been approved for RA in Korea: etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, golimumab, tocilizumab, and abatacept, and analyzed the changes in market share of biosimilars among the bDMARDs after their introduction. Overall trends of medical costs for each bDMARD were presented over the 10-year period.
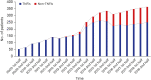
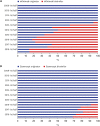
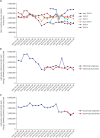
Results: Since the introduction of the biosimilar TNFis in 2012, the proportion of their use among bDMARDs steadily increased to 15.8% in 2018. While there has been a gradual increase in the use of biosimilar TNFis, the use of the corresponding originators has been decreasing. The introduction of biosimilar TNFis has resulted in a decrease in the medical costs of patients using either originator or biosimilar TNFis.
Conclusion: In Korea, the proportional use of biosimilar TNFis has gradually increased since their introduction. The availability of less expensive biosimilar TNFis seems to have brought about a decrease in the medical costs of users of the originators.
Keywords: Arthritis, Rheumatoid; Biologics; Biosimilar; Trend.
© 2021 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Yoon-Kyoung Sung has received research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Pfizer, and JW Pharmaceutical. Soo-Kyung Cho, Sun-Young Jung, Hyoungyoung Kim, Yeo-Jin Song, and Kyungeun Lee have nothing to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Infliximab and Etanercept Biosimilars on Biological Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs Utilisation and NHS Budget in the UK.BioDrugs. 2017 Dec;31(6):533-544. doi: 10.1007/s40259-017-0252-3. BioDrugs. 2017. PMID: 29127626
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and their biosimilars in patients with rheumatoid arthritis having an insufficient response to methotrexate : A network meta-analysis.Z Rheumatol. 2023 Apr;82(3):248-255. doi: 10.1007/s00393-021-01041-z. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Z Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 34223982 English.
-
Cost-Effectiveness of Early Treatment with Originator Biologics or Their Biosimilars After Methotrexate Failure in Patients with Established Rheumatoid Arthritis.Adv Ther. 2019 Aug;36(8):2086-2095. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-00986-7. Epub 2019 May 30. Adv Ther. 2019. PMID: 31148057 Free PMC article.
-
Biosimilars for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: economic considerations.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015;11 Suppl 1:S43-52. doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2015.1090313. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26395836 Review.
-
Anti-TNF biosimilars in psoriasis: from scientific evidence to real-world experience.J Dermatolog Treat. 2020 Dec;31(8):794-800. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1610553. Epub 2019 May 16. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020. PMID: 31094242 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term effectiveness and safety of infliximab-biosimilar: A multicenter Phoenix retrospective cohort study.PLoS One. 2023 Sep 12;18(9):e0288393. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288393. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37699041 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Persistence and Incidence of Active Tuberculosis of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Inhibitors Versus Tocilizumab as the First-Line Biological Treatment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Nationwide Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Analysis.Rheumatol Ther. 2024 Aug;11(4):881-895. doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00674-1. Epub 2024 May 20. Rheumatol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38769252 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced economic disparity in biologics use for psoriasis after introducing the reducing copayment program.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 20;14(1):4139. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54447-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38374130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scheinberg MA, Kay J. The advent of biosimilar therapies in rheumatology--“O brave new world”. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(7):430–436. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(6):960–977. - PubMed
-
- Improving access to biosimilars in low-income countries. Lancet. 2017;389(10082):1860. - PubMed
-
- QuintilesIMS. The impact of biosimilar competition in Europe. [Updated 2017]. [Accessed April 15, 2021]. http://ec.europa.eu/growth/content/impact-biosimilar-competition-price-v....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

