Hospital Readmission Risks Screening for Older Adult with Stroke: Tools Development and Validation of a Prediction
- PMID: 34032150
- PMCID: PMC8155787
- DOI: 10.1177/00469580211018285
Hospital Readmission Risks Screening for Older Adult with Stroke: Tools Development and Validation of a Prediction
Abstract
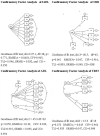
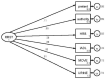
Hospital readmission of stroke elderly remains a need for detecting preventable risks. This study aims to develop a Readmission Stroke Screening Tool or RRST. The mixed research design was employed, phase1; systematic reviews from 193 articles extracting to be 14 articles, 9 experts' consensus, and try out the RRST Internal consistency; IOC = .93, ICC = between .93 and .56, phase 2; Data collecting 150 of strokes patients in the stroke units during 2019 to 2020; 30 nurses employed the RRST to screen stroke elderly before discharge. Statistical analysis, Exploring Principal Factor Analysis to test the best predictor factor, and Confirmatory Factor Analysis to test the model identity were employed. Results: The multi-domain RRST; 4 factors: Intra, inter, and external factors of patients can predict the hospital readmission of Stroke elderly at a high level in 28 days. The ADL: Activities in the Daily life domain was the highest level of predicting (Eigen Value = 6.76, 1.15, Variances = 79.19%) significantly. 53.3% of user nurses reflected; the RRST tool's effectiveness was achievable in usefulness, benefit, accuracy, and easy to use; however, the rest users identified to improve the RRST easier and quicker. Conclusion; The new RRST; can predict the high-risk readmission effectively = 92.5%. User nurses satisfied the RRST predicted quality. the multi-domain RRST could be detecting the Thai Stroke's high-risk group for reducing avoidable risks, suggestion; more effort will be investigated prospectively in readmission by expanded volume of the Asian' Stroke elderly for increasing accuracy predicting and extended tool quality utilized standard scored correctly.
Keywords: Asian’ Stroke elderly; prediction of readmission; risk screening; tool development; tool quality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ingall T. Stroke: incidence, mortality, morbidity, and risk. J Insur Med. 2004;36:143-152. - PubMed
-
- Healthcare Accreditation Institute. Criteria Evaluation and Certification Primary Stroke Center. Public Organization, Ministry of Public Health; 2015. (in Thai)
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

