High-resolution magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry imaging of the human larynx
- PMID: 34032275
- PMCID: PMC8349453
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.13451
High-resolution magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry imaging of the human larynx
Abstract
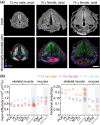
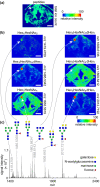
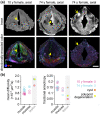
High-resolution, noninvasive and nondestructive imaging of the subepithelial structures of the larynx would enhance microanatomic tissue assessment and clinical decision making; similarly, in situ molecular profiling of laryngeal tissue would enhance biomarker discovery and pathology readout. Towards these goals, we assessed the capabilities of high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation-mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) imaging of rarely reported paediatric and adult cadaveric larynges that contained pathologies. The donors were a 13-month-old male, a 10-year-old female with an infraglottic mucus retention cyst and a 74-year-old female with advanced polypoid degeneration and a mucus retention cyst. MR and molecular imaging data were corroborated using whole-organ histology. Our MR protocols imaged the larynges at 45-117 μm2 in-plane resolution and capably resolved microanatomic structures that have not been previously reported radiographically-such as the vocal fold superficial lamina propria, vocal ligament and macula flavae; age-related tissue features-such as intramuscular fat deposition and cartilage ossification; and the lesions. Diffusion tensor imaging characterised differences in water diffusivity, primary tissue fibre orientation, and fractional anisotropy between the intrinsic laryngeal muscles, mucosae and lesions. MALDI-MS imaging revealed peptide signatures and putative protein assignments for the polypoid degeneration lesion and the N-glycan constituents of one mucus retention cyst. These imaging approaches have immediate application in experimental research and, with ongoing technology development, potential for future clinical application.
Keywords: Reinke's oedema; diffusion tensor imaging; glycomics; molecular imaging; mucus retention cyst; polypoid degeneration; proteomics; vocal fold; whole-larynx histology.
© 2021 Anatomical Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
-
Translating state-of-the-art spinal cord MRI techniques to clinical use: A systematic review of clinical studies utilizing DTI, MT, MWF, MRS, and fMRI.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Dec 4;10:192-238. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.11.019. eCollection 2016. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 26862478 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical Proprioceptors Are Largely Absent in the Intrinsic Laryngeal Muscles of the Rat Larynx.J Comp Neurol. 2025 Jun;533(6):e70062. doi: 10.1002/cne.70062. J Comp Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40524482 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prognostic Prediction of Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy.Dev Neurosci. 2024;46(1):55-68. doi: 10.1159/000530938. Epub 2023 May 10. Dev Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 37231858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
Cited by
-
On-tissue amidation of sialic acid with aniline for sensitive imaging of sialylated N-glycans from FFPE tissue sections via MALDI mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022 Jul;414(18):5263-5274. doi: 10.1007/s00216-022-03894-y. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35072748 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry imaging of N-linked glycans: Fundamentals and recent advances.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2024 Jun 27:10.1002/mas.21895. doi: 10.1002/mas.21895. Online ahead of print. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2024. PMID: 38934211 Review.
-
Furosemide-induced systemic dehydration alters the proteome of rabbit vocal folds.J Proteomics. 2022 Feb 10;252:104431. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2021.104431. Epub 2021 Nov 23. J Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 34823036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong, W.B. , Ridgway, J.M. , Vokes, D.E. , Guo, S. , Perez, J. , Jackson, R.P. et al. (2006) Optical coherence tomography of laryngeal cancer. Laryngoscope, 116, 1107–1113. - PubMed
-
- Burns, J.A. , Kim, K.H. , deBoer, J.F. , Anderson, R.R. & Zeitels, S.M. (2011) Polarization‐sensitive optical coherence tomography imaging of benign and malignant laryngeal lesions: An in vivo study. Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, 145, 91–99. - PubMed
-
- Burns, J.A. , Zeitels, S.M. , Anderson, R.R. , Kobler, J.B. , Pierce, M.C. & de Boer, J.F. (2005) Imaging the mucosa of the human vocal fold with optical coherence tomography. Annals of Otology, Rhinology, and Laryngology, 114, 671–676. - PubMed
-
- Calligaris, D. , Feldman, D.R. , Norton, I. , Brastianos, P.K. , Dunn, I.F. , Santagata, S. et al. (2015) Molecular typing of meningiomas by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging for surgical decision‐making. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 377, 690–698. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

