Combined healthy lifestyle score and risk of epigenetic aging: a discordant monozygotic twin study
- PMID: 34032609
- PMCID: PMC8202852
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203022
Combined healthy lifestyle score and risk of epigenetic aging: a discordant monozygotic twin study
Abstract
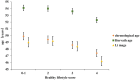
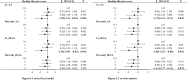
We investigated whether lifestyle influences epigenetic aging in 143 monozygotic twin pairs discordant for the combined healthy lifestyle score. Twins were scored for four lifestyle factors as unhealthy or healthy; non-smoker, moderate drinker, adequate fruit and vegetable intake, and sufficient physical activity. The combined healthy lifestyle score was calculated for each participant by summing the binary score for each factor. Individual and co-twin analyses were used to assess the relationship between single or combined lifestyle scores, along with DNA methylation age acceleration (AA) calculated using Horvath's and Li's epigenetic clocks, focusing on AA and intrinsic epigenetic age acceleration (IEAA) measures. Compared with the twins that scored no or one healthy lifestyle point, those who scored four healthy lifestyle points had lower Li_IEAA with similar results observed in the co-twin analysis. No significant relationships were found in analyses based on Horvath's clock, although the direction of correlations was consistent with that determined using Li's clock. Smoking and drinking did not significantly affect DNA methylation AA; however, physical activity and intake of vegetables and fruits did, although the influence varied depending on the epigenetic clock. Our findings suggest that a healthy lifestyle may be an important way to delay aging and prevent age-related diseases.
Keywords: Chinese; DNA methylation age; epigenetic aging; healthy lifestyle; twin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does the epigenetic clock GrimAge predict mortality independent of genetic influences: an 18 year follow-up study in older female twin pairs.Clin Epigenetics. 2021 Jun 13;13(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01112-7. Clin Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 34120642 Free PMC article.
-
Leisure-time physical activity and DNA methylation age-a twin study.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 Jan 19;11(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0613-5. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 30660189 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Alcohol Consumption With Epigenome-Wide DNA Methylation and Epigenetic Age Acceleration: Individual-Level and Co-twin Comparison Analyses.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Feb;45(2):318-328. doi: 10.1111/acer.14528. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 33277923 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Psychosocial Stress from Life Trauma and Racial Discrimination on Epigenetic Aging-A Systematic Review.Biol Res Nurs. 2022 Apr;24(2):202-215. doi: 10.1177/10998004211060561. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Biol Res Nurs. 2022. PMID: 35102751 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic clock: A promising biomarker and practical tool in aging.Ageing Res Rev. 2022 Nov;81:101743. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101743. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Ageing Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 36206857 Review.
Cited by
-
Social determinants of health and epigenetic clocks: Meta-analysis of 140 studies.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 8:2025.05.08.25327207. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.08.25327207. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40385415 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Active longevity and aging: dissecting the impacts of physical and sedentary behaviors on longevity and age acceleration.Geroscience. 2025 Jun;47(3):3525-3538. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01329-3. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 39230773 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating DNA Methylation Measures of Biological Aging into Social Determinants of Health Research.Curr Environ Health Rep. 2022 Jun;9(2):196-210. doi: 10.1007/s40572-022-00338-8. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2022. PMID: 35181865 Review.
-
Human age reversal: Fact or fiction?Aging Cell. 2022 Aug;21(8):e13664. doi: 10.1111/acel.13664. Epub 2022 Jul 2. Aging Cell. 2022. PMID: 35778957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lifestyle Factors as Perceived Causes of Psychological Distress: Implications for Mental Health Stigma.Am J Lifestyle Med. 2025 Apr 14:15598276251332887. doi: 10.1177/15598276251332887. Online ahead of print. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2025. PMID: 40241686 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen BH, Marioni RE, Colicino E, Peters MJ, Ward-Caviness CK, Tsai PC, Roetker NS, Just AC, Demerath EW, Guan W, Bressler J, Fornage M, Studenski S, et al.. DNA methylation-based measures of biological age: meta-analysis predicting time to death. Aging (Albany NY). 2016; 8:1844–65. 10.18632/aging.101020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

